Figure 18.3.
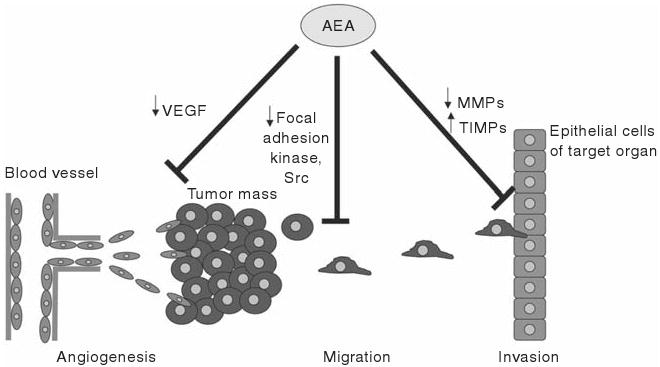
AEA inhibits other aspects of tumorigenesis such as angiogenesis, tumor cell migration, and tumor invasion. AEA inhibits angiogenesis via a decrease in VEGF expression, whereas the decrease in migration is thought to be via a decrease in the activation of focal adhesion kinases and src kinase, both of which are thought to be involved in cell migration and metastasis. Lastly, AEA inhibits tumor cell invasion by decreasing the expression of proteins responsible for breaking down the extracellular matrix of the target organ, such as MMPs and increasing the expression of the tissue inhibitors of MMPs.
