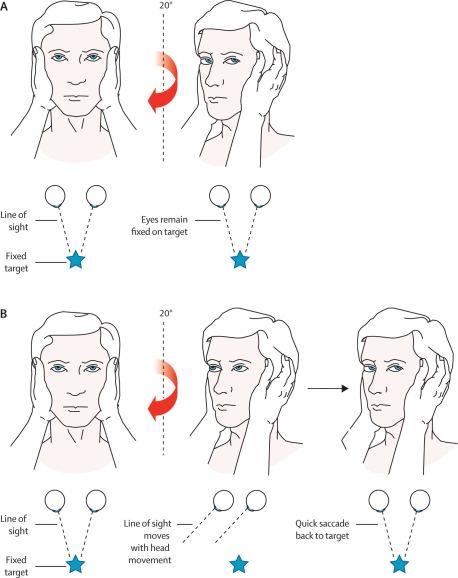
Figure 1.
Head impulse test. A: The right ear has intact peripheral vestibular function. When the head is turned to the right, the vestibulo-ocular reflex moves the eyes to maintain visual fixation. B: The right ear now has impaired vestibular function. When the head is turned to the right, the eyes move with it, breaking visual fixation, and a refixation saccade is seen as the eyes dart back to the examiner’s face. This indicates a peripheral vestibular disorder on the right side. Reprinted from The Lancet Neurology, Vol. 7, Edlow JA, Newman-Toker DE, and Savitz SI, Diagnosis and initial management of cerebellar infarction”, Page No. 959, Copyright 2008, with permission from Elsevier.