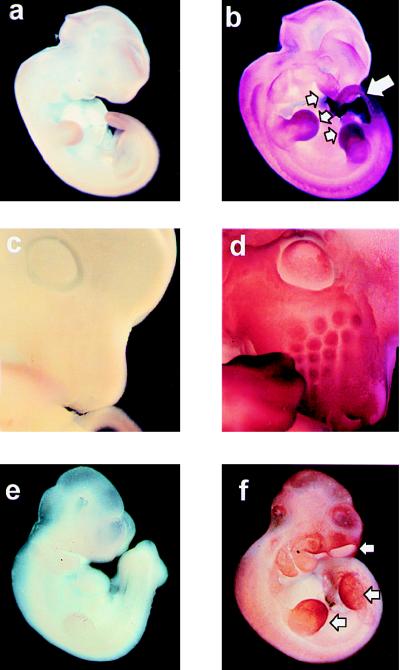
Figure 2.
Expression of mTERT mRNA in mouse embryos. (a and b) Eleven-day wild-type embryos hybridized with sense (a) or antisense (b) mTERT-derived riboprobes. b shows generalized expression of mTERT. Regions of particularly high levels of mTERT mRNA are indicated with arrows. (c and d) Detail of the head of a 12-day wild-type embryo hybridized with sense (c) or antisense (d) mTERT-derived riboprobes. d shows high levels of mTERT mRNA in the developing hair follicles of the nares. (e and f) Ten-and-one-half-day mTR−/− embryos hybridized with sense (e) or antisense (f) mTERT-derived riboprobes. The pattern and intensity of the mTERT mRNA signal are similar in b and f.