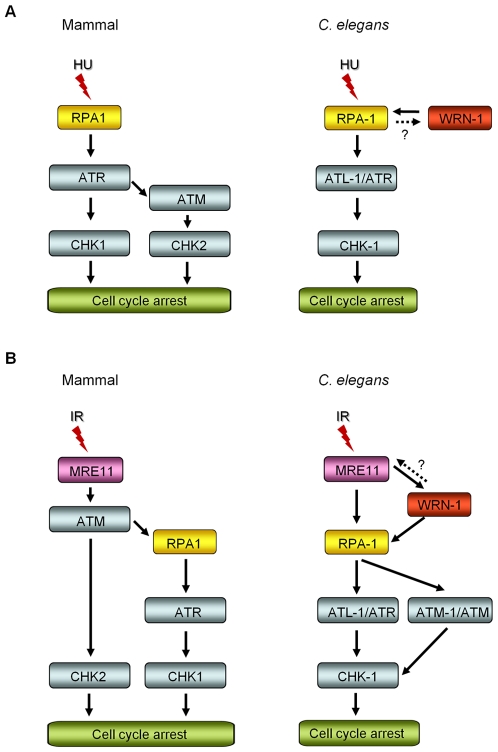
Figure 6. Comparison of DNA replication and damage checkpoint pathways between mammals and C. elegans, and roles of the C. elegans WRN homolog in these pathways.
(A) After DNA replication inhibition by hydroxyurea (HU), ATM-CHK2 activation is induced in the downstream of ATR in mammals, in addition to ATR-CHK1 activation [51]. In C. elegans, the nuclear focus formation of RPA-1 and WRN-1 are interdependent, however RPA-1 knockdown may have indirectly affected WRN-1 foci by reducing the number of replication forks. ATR/ATL-1 is inserted between RPA-1 and CHK-1, because it was positioned below RPA-1 by Garcia-Muse and Boulton [26]. (B) Ionizing radiation (IR) induces ATR-CHK1 activation in the downstream of ATM, as proposed by Jazayeri et al. [44] in mammals. In C. elegans, the nuclear localization of WRN-1 in response to IR is affected by MRE-11 and is a prerequisite for efficient RPA-1 focus formation. It needs to be determined whether WRN-1 conversely affects the nuclear localization or function of MRE-11, as labeled by a question mark. The nuclear accumulation of ATM requires WRN-1 and RPA-1, as well as MRE-11. ATR/ATL-1 is positioned below RPA-1, as proposed by Garcia-Muse and Boulton [26], and is required for effective cell cycle arrest (Figure 5A). CHK-1 is located below ATR, because it was shown to be essential for cell cycle arrest in response to IR by Kalogeropoulos et al. [52] and also in Figure 5A.