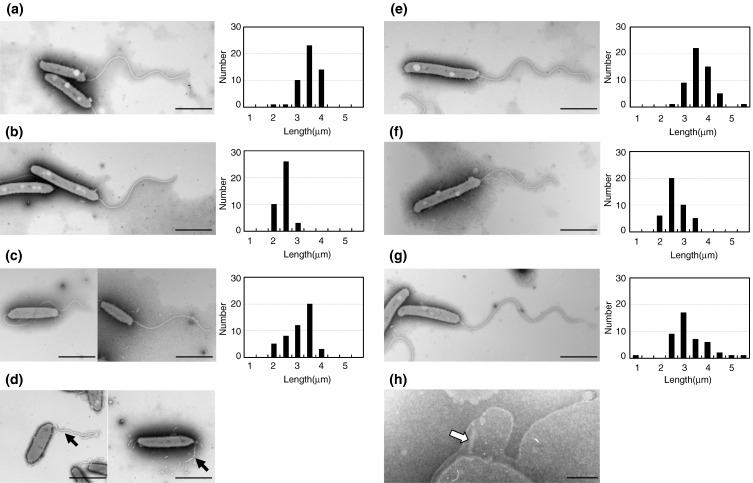
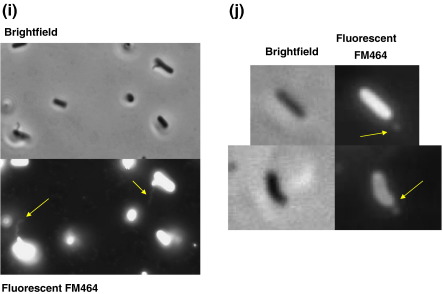
Fig. 2.
EM images of flagella from flagellin knockout mutants: (a) wild-type 109J, (b) fliC1, (c) fliC2, (d) fliC3, (e) fliC4, (f) fliC5, and (g) fliC6 mutants and (h) a hook–basal body complex in the fliC3 mutant. Bars represent 1 μm except for (h) which is 100 nm. Histograms showing the distribution of flagellar lengths at 24 h of incubation for each strain are shown to the right of EM images. Fluorescent microscope images of (i) Bdellovibrio and E. coli RP437 (both highly motile in this culture) mixed together and stained with FM464 membrane stain. Only the Bdellovibrio (which are attached to the E. coli, preying on them) show flagellar staining, despite the E. coli having many non-sheathed flagella that do not stain. (j) B. bacteriovorus 109J fliC3 mutant cells stained with the FM464, showing disordered membrane bleb at the pole of the cell.