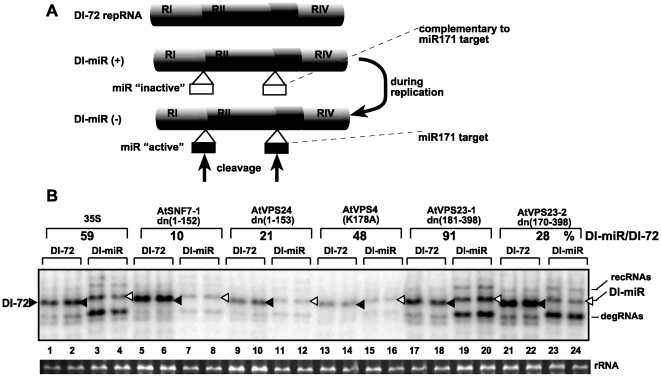
Figure 4. Increased sensitivity of repRNA replication to targeted degradation by RNAi in plants expressing dominant negative ESCRT-III mutants.
(A) A schematic representation of constructs used as repRNAs. Two copies of the 21 nt long miR171 target sequence were inserted into DI-72 repRNA to generate DI-miR repRNA as shown. Note that both copies of the miR171 target sequence were present in the (−)strand RNA generated during repRNA replication only in plants agroinfiltrated with constructs expressing p33/p92/dominant negative ESCRT proteins and DI-72 or DI-miR repRNAs. (B) Northern blot analysis shows reduced accumulation of DI-miR repRNA in N. benthamiana plants expressing dominant negative ESCRT-III or Vps4p mutants. DI-72 repRNA is depicted with a black arrowhead, while DI-miR repRNA is marked with an open arrowhead. The percentage of DI-miR repRNA accumulation was calculated based on DI-72 repRNA levels (taken as 100% for each set). Note that the low level DI-miR repRNA accumulation suggests that the RNAi machinery destroyed most of the (−)repRNA present in the replicase complex. recRNA represents recombinant repRNAs, while degRNA is derived from partially degraded repRNA. Note that degRNA can replicate in plants, so it does not represent the original cleaved repRNA.