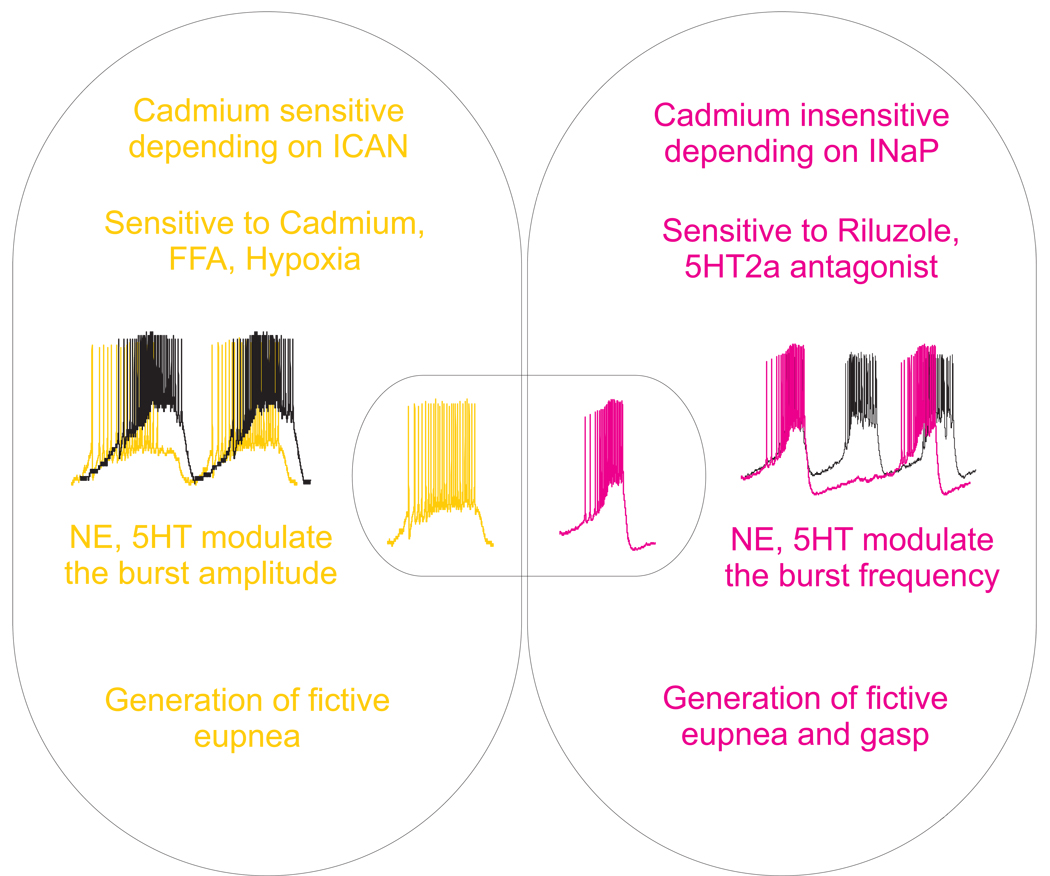
Figure 1. Modulation of pacemaker intrinsic properties.
In slices preparation containing the preBötC (650 µM thick slice, the potassium concentration raised at 8mM, bubbled with 95% O2-5% CO), two types of inspiratory neurons that express pacemaker properties have been identified. The bursting mechanism of one type depends on calcium-activated non-selective cation current and they are referred as “cadmium sensitive” (CS) pacemaker neurons (in yellow). The other type of pacemaker neurons have a bursting mechanism that depends on the persistent sodium current, these are so-called cadmium insensitive (CI) pacemaker neurons (in red). The two types of pacemaker neurons are proposed to play different roles in the modulation of the different respiratory like patterns. Bioamines such as, 5-HT and NE differentially modulate the different types of pacemaker neurons.