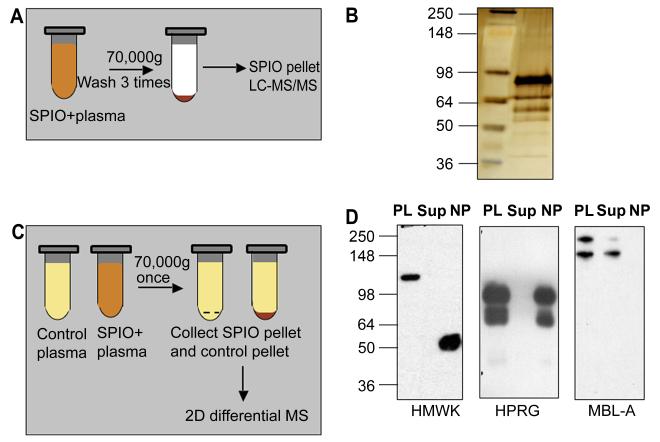
Figure 1. Protein binding and effect of plasma proteins on SPIO clearance and macrophage uptake.
A, Schematic representation of one-dimensional proteomic analysis of plasma proteins bound to SPIO. B, Silver stained SDS-PAGE. Proteins were eluted from SPIO using the above procedure and analyzed by LC-MS/MS (Table 1). Left lane, SeeBlue Plus2 standard size marker (Invitrogen); right lane, eluted proteins. C, Schematic representation of two-dimensional differential proteomics procedure used to identify plasma proteins that bind to SPIO. See Methods for complete description of the procedure. D, Depletion of some of the binding proteins from plasma after incubation with SPIO. The particles were incubated with plasma as described in Methods, pelleted using ultracentrifuge and the supernatant was analyzed by western blotting. Each gel included plasma proteins before incubation with SPIO (PL), supernatant after pelleting the particles (Sup) and the particles (NP) washed by additional 4 rounds of ultracentrifugation with PBS. HMWK undergoes cleavage on the particle surface (uncleaved size 120 kDa) to form activated kininogen (HKa). To detect MBL-A, the proteins were separated and detected under non-reducing conditions. Note that MBL-A was not detectable on SPIO, while it was depleted from plasma.