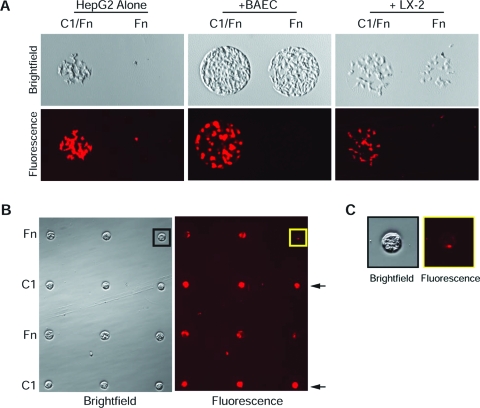
FIG. 5.
Extracellular matrix (ECM) arrays support co-cultures of HepG2 cells with bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) or LX-2 hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). (A) ECM microarrays support co-cultures of HepG2 hepatocytes were prestained with CellTracker Orange CMTMR (HepG2-CMTMRs) with BAECs or LX-2 HSCs. Sequential seeding with BAECs (middle panel) or LX-2 HSCs (right panel) onto the 64 ECM combinatorial protein arrays produced co-cultures with HepG2 cells, which do not attach to fibronectin (Fn) spots (left panel). (B) ECM arrays composed of alternating rows of Fn and rat collagen I were sequentially seeded with BAECs and HepG2-CMTMRs to establish co-cultures patterns. Brightfield images show the pattern and boundary of the cell cultures in the 4 × 4 array. Fluorescent images show that rows of rat collagen I (black arrows) are occupied by HepG2-CMTMRs and that rows of Fn are cultured with both cell types. (C) Magnified images of boxed regions from (B). Brightfield (black box) and fluorescence (yellow box) image showing a Fn island occupied mainly by BAECs. Brightfield images were obtained using an Olympus digital camera mounted on a Nikon TS100 microscope. Fluorescent images were acquired using an Olympus IX71 inverted fluorescent microscope. Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/ten.