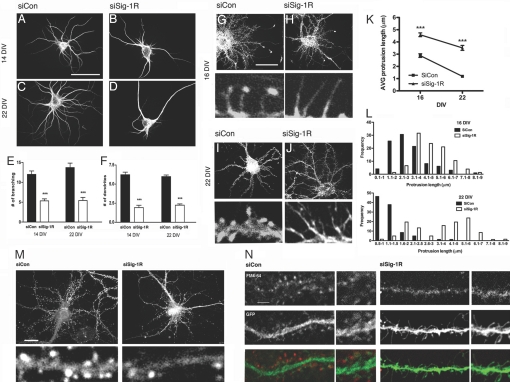
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of dendritic morphogenesis in Sig-1R-knockdown hippocampal neurons. (A–F) Effects of siSig-1R-tf on dendrite formation. Neurons were transfected with siRNAs on DIV 7 and were stained on 14 or 22 DIV with anti-MAP-2B antibodies. The number of established primary dendrites and branches were counted. Primary dendrites are defined as neurites originating from the neuronal soma and are at least longer than two times the diameter of the cell body. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) ***P < 0.001; n = 3, five to 10 neurons were quantified in each individual experiment. (G–J) Effect of siSig-1R-tf on spine formation. Neurons were transfected on DIV 7 with siCon (G and I) or siSig-1R (H and J) vectors in combination with EGFP. Neurons were stained with rhodamin phalloidin for F-actin. Note elongated filopodia in si-Sig-1R-tf neurons. (K and L) Quantitative assessments were made of the effects of siSig-1Rs on protrusion length, dendrite branching, and filopodium formation. The control neurons at DIV 22 had protrusions mostly <2 μm in length and mushroom shaped, which is characteristic of dendritic spines, whereas the siRNA neurons failed to retract protrusions (i.e., exhibited elongated filopodia). Protrusions equals dendritic spines plus filopodia. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) ***P = 0.0002; n = 2, at least 20 neurons were captured in each experiment, and two to three dendrites were randomly selected from each neuron for counting of protrusions. (M) Synaptophysin immunostaining. (N) Effects of siSig-1Rs on synaptic activity. FM4–64 (red)-labeled neurons were depolarized with KCl for measurement of synaptic activity. (Scale bars, M 20 μm and N 5 μm.)