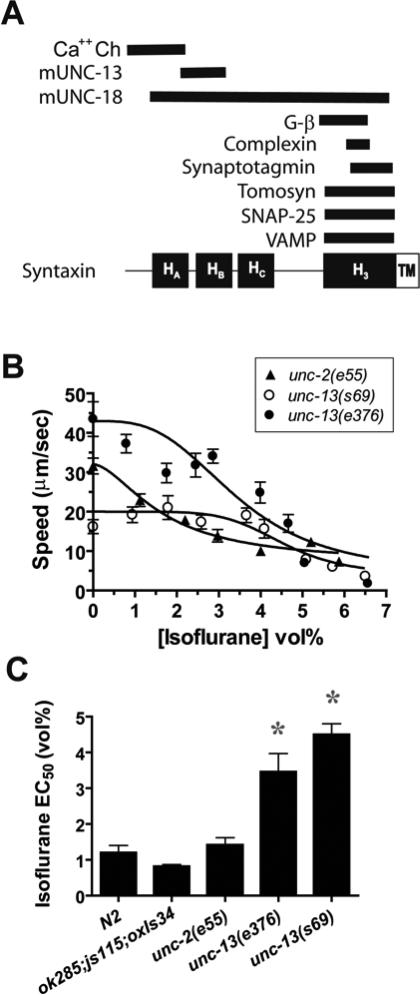
Fig. 4.
UNC-13 is required for isoflurane sensitivity. (A) Proteins known to bind to syntaxin. The proteins are aligned with the syntaxin region, with which it binds. Ca++ Ch – N- and P- type calcium channels 5,6, mUNC-18 – mammalian UNC-18 7,8, mUNC-13 – mammalian UNC-13 9, Gβ – β-subunit of a G-protein 5, complexin 10,11, synaptotagmin 7, tomosyn 12, SNAP-25 13, Vesicle-associated Membrane Protein (VAMP) 13,14 (B) Isoflurane sensitivity of the locomotion of strains with loss-of-function mutations in unc-13 and unc-2. The full genotypes are: tom-1(ok285null) unc-13(s69lf);unc-64(js115 null);oxIs34[unc-64(L166A/E167A);Pmyo-2::GFP] , tom-1(ok285null) unc-13(e376lf);unc-64(js115 null);oxIs34[unc-64(L166A/E167A);Pmyo-2::GFP]/+, and unc-2(e55 null). Each point represents the mean ± sem of 10 animals. (C) Summary of Isoflurane EC50's ± SE of the fit from B. tom-1(ok285);unc-64(js115);oxIs34 is the genetic background for the unc-13 mutants and is shown for comparison along with the wild type strain N2. * - p < 0.01 vs N2 and ok285;js115;oxIs34