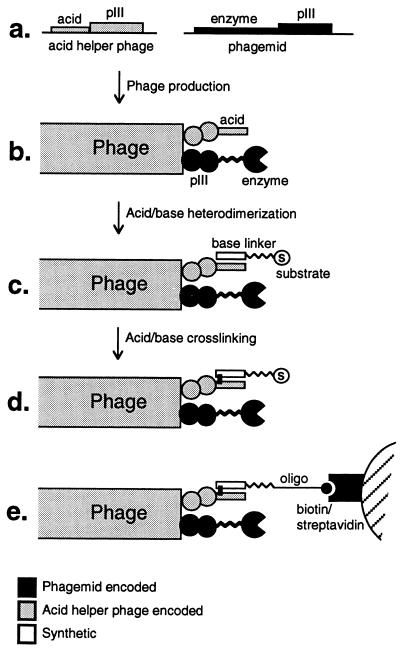
Figure 2.
Covalent attachment of substrate to the pIII protein on phage. (a) DNA encoding the acid peptide sequence and a C-terminal cysteine was fused to the N-terminal end of gene gIII, to form the acid helper phage. A phagemid encodes the protein library in fusion with the pIII protein. (b) Phage production leads to phage particles displaying the phagemid encoded protein; the pIII proteins have acid peptide extensions. (c) Coiled–coil formation of the acid and base peptides noncovalently attaches the substrate to the phage pIII protein. (d) Removal of the reducing agent leads to crosslinking of acid and base peptides through their C-terminal cysteines. (e) In the present study phages displaying SNase are attached to streptavidin beads through a 5′-biotinylated, single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide. Phages displaying active enzyme are released by cleavage of the oligodeoxynucleotide in an intramolecular reaction.