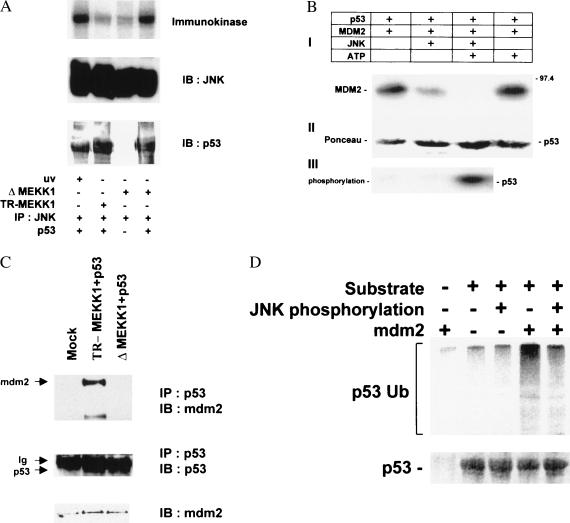
Figure 2.
(A) P53 is phosphorylated by JNK in the immunokinase assay. Soluble bacterially expressed p53 was subjected to phosphorylation by JNK immunopurified from 293T cells treated with UV irradiation or cotransfected with either TR-MEKK1 or ΔMEKK1 constructs as indicated. (Top) Autoradiograph. Immunoblots depicting the amounts of kinase (Middle) and substrate (Bottom) in the samples. (B) mdm2 binding to p53 is inhibited by JNK. Bead-bound human hisp53 was incubated with purified Mdm2 and JNK, as indicated, in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP (50 cpm/fmol; Amersham) and 50 μM ATP in kinase buffer for 15 min at 30°C. P53-associated proteins were extensively washed before analysis via immunoblots with antibodies to mdm2 (2A10) was performed (I). (II) Ponceau S stain of the same membrane revealing the amounts of hisp53 used throughout this experiment. (III) Autoradiograph depicting p53 phosphorylation. (C) In vivo association between p53 and Mdm2. p53 null cells (10.1) were transfected with wild-type p53 and either TR-MEKK1 or ΔMEKK1 constructs. Protein extracts were prepared 36 h after transfection and 8 h after treatment with lactacystin (5 μM). p53 proteins were immunoprecipitated with antibody to p53 and immunoprecipitated material was subjected to immunoblot with antibodies to Mdm2 (Top). (Middle) The same blot reprobed with p53 antibody. (Bottom) The level of Mdm2 expressed in whole-cell extracts. (D) Phosphorylation of p53 by JNK abrogates Mdm2-mediated targeting for p53 ubiquitination in vitro. Bead-bound hisp53 was phosphorylated by JNK, incubated with Mdm2 (as indicated), washed, and subjected to in vitro ubiquitination reaction in the presence of HA-tagged ubiquitin as described in Materials and Methods. (Top) Immunoblot with anti-HA antibody. (Bottom) The input of p53 detected by Ponceau S staining.