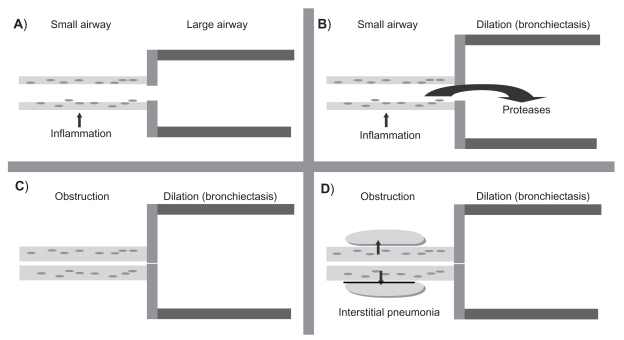
Figure 2.
Pathologic changes in follicular bronchiectasis as described by Whitwell. A) The first process involves infection of the small airways. B) This leads to the release of inflammatory mediators such as proteases which damage the large airways resulting in bronchial dilation and bronchiectasis. C) Infection drives progressive inflammation in the small airways which become thicker from a combination of cell-mediated inflammatory infiltrate and lymphoid follicles resulting in obstruction. D) The final process involves the spread of inflammation beyond the airways resulting in interstitial pneumonia.