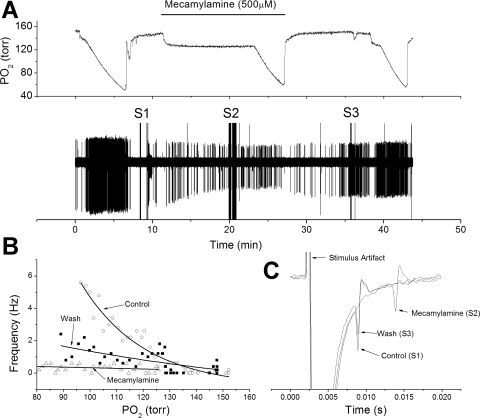
Fig. 3.
High-dose mecamylamine appears to reduce chemoreceptor nerve response to hypoxia in some chemoreceptor units. A: polygraphic recordings as in Fig. 1. B: frequency/Po2 response relationship before (○), during (△), and following (■) perfusion with mecamylamine (500 μM). Note greatly reduced AP rate during hypoxia in the presence of mecamylamine. C: expanded, overlaid traces during orthodromic stimulation. Mecamylamine slowed conduction velocity and reduced AP height. It also led to AP propagation failure as observed during S2 (see Fig. 5).