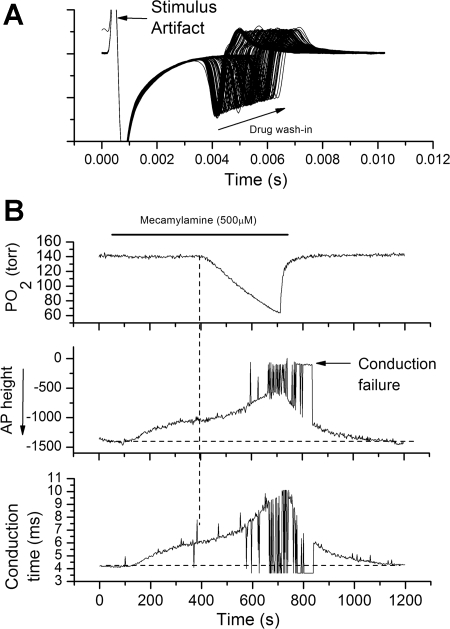
Fig. 5.
High dose of mecamylamine reduces AP height, slows AP velocity, and leads to AP propagation failure during hypoxia. A: overlaid polygraphic sweeps during application of stimulus pulses to the carotid body during 5-min wash-in of mecamylamine (arrow). Time is on the abscissa and voltage on the ordinate. Mecamylamine slowed nerve conduction and reduced AP height. B: hypoxia (vertical dashed line) in the presence of mecamylamine further slows conduction velocity, reduces AP height, and leads to AP conduction failure. AP height and conduction time were determined by peak detection program (Clampfit9) in the poststimulus period. Conduction failure is indicated by a near zero AP height. AP detection and height were measured in the negative-going phase in the 10-ms poststimulus period.