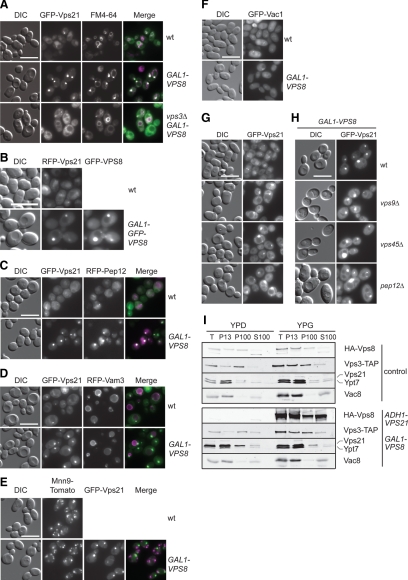
Figure 1.
The Vps21-compartment resembles an endosomal structure. (A) Localization of GFP-Vps21 in the absence of VPS3. Wild-type and Vps8-overexpressing cells in the presence or absence of VPS3 were grown to logarithmic phase in YPG medium, stained with FM4-64, harvested, washed once with PBS buffer, and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Size bar, 10 μm. (B) Colocalization of RFP-Vps21 and overexpressed GFP-Vps8. The top panel shows the localization of RFP-Vps21 in the wild-type background. In the bottom panel, RFP-Vps21 and GFP-Vps8 (PHO5-RFP-Vps21 GAL1-GFP-VPS8) were coexpressed in wild-type cells. Cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy as described in A. Size bar, 10 μm. (C–F) Colocalization of Vps21 with different organelle protein markers after Vps8 overproduction. RFP-Pep12 (C), RFP-Vam3 (D), or Mnn9-Tomato (E) were coexpressed with GFP-Vps21 in wild-type and Vps8-overexpressing cells and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. In F, GFP-tagged Vac1 was localized in both cell types. Microscopy analysis was performed as in A. (G and H) Localization of GFP-Vps21 in the indicated class D vps mutant strains in absence (G) or presence (H) of overexpressed Vps8. The cells were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy as in A. Size bar, 10 μm. (I) Subcellular distribution of CORVET and endolysosomal Rab GTPases. Lysed spheroplasts from cells expressing C-terminally TAP-tagged Vps3 and HA-tagged Vps8 (control) or from cells overexpressing Vps21 and Vps8 (ADH-VPS21 GAL1-HA-VPS8) were subjected to two differential centrifugations, resulting in a 13,000 × g pellet (P13), a 100,000 × g pellet (P100), and a final supernatant (S100). Fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against the indicated proteins.