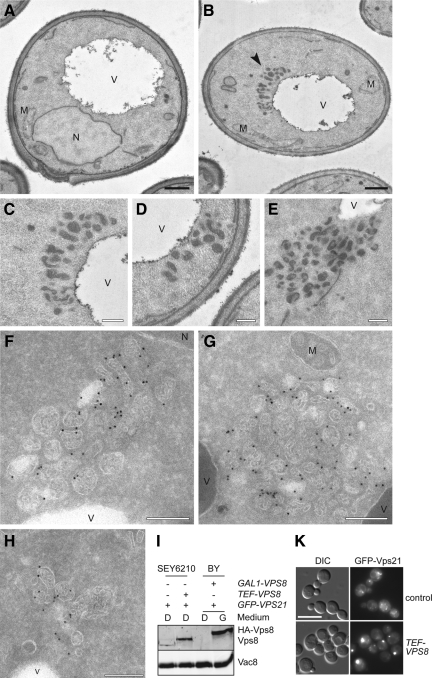
Figure 2.
Ultrastructural analysis reveals the clustering of LE structures. (A–H) Ultrastructural analyses. The SEY6210 PHO5-GFP-VPS21 (A), SEY6210 PHO5-GFP-VPS21 TEF1-VPS8 (B–E), SEY6210 TEF1-GFP-VPS8 ADH1-VPS21 (F and G), and SEY6210 PHO5-GFP-VPS21 TEF1-HA-VPS8 (H) strains were grown to exponential phase and embedded in Spurr's resin (A–E) or prepared for IEM (F–H) as described in Material and Methods. Cryosections (F–H) were first incubated with goat anti-GFP antibodies (Rockland, Gilbertsville, PA) and then with 15-nm gold particles conjugated to protein A. Arrowheads in B indicate the abnormal structures observed in those cells. (C to E) The clusters of vesicles observed in cells overexpressing Vps8. Clusters of small MVBs were observed in proximity of the vacuole limiting membrane. V, vacuole; M, mitochondrion; N, nucleus. Black bar, 500 nm; white bar, 200 nm. (I) Protein expression levels. P13 fractions obtained from cells grown in glucose- or galactose-containing medium were analyzed by separating equal amounts of proteins by SDS-PAGE and by decorating Western blots with antibodies recognizing Vps8 and Vac8 (loading control). (K) Formation of the Vps21 compartment in the SEY6210 strain background upon Vps8 overproduction. Localization of GFP-Vps21 in wild-type and TEF1 promoter driven HA-tagged Vps8-expressing cells. Samples were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy as described in Figure 1A. Size bar, 10 μm.