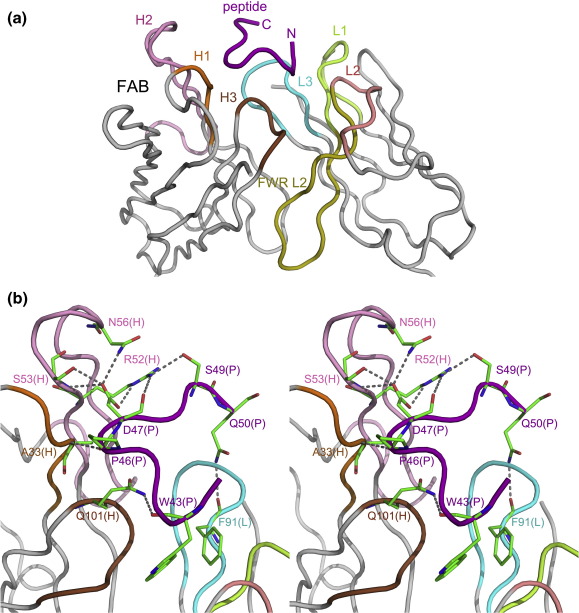
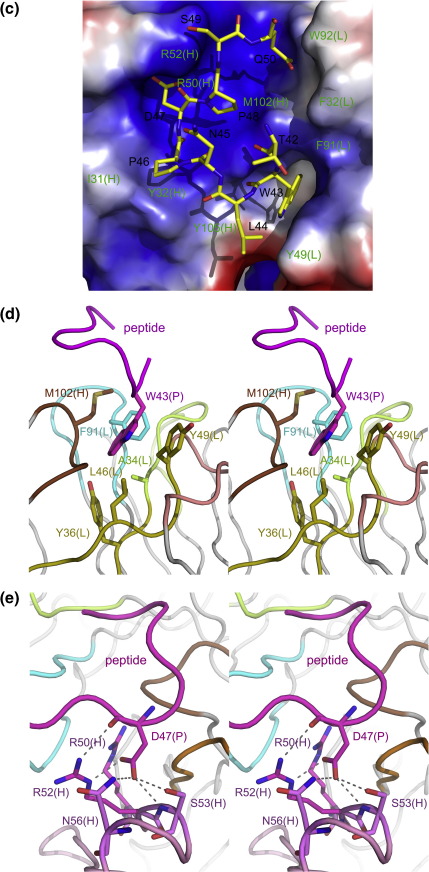
Fig. 2.
The interactions between the 23C3 Fab and the bound peptide. (a) An enlarged view of the interface surface. The peptide is bound at a pocket formed mainly by CDRs and interacts with CDRs L1, L3, H1, H2, and H3 and FWR L2. The Fab CDR L1 is colored lemon; L2, salmon; L3, cyan; H1, orange; H2, pink; H3, brown; FWR L2, olive; and other FWRs, silver. The peptide is colored purple. (b) A stereo view showing the hydrogen bonds between residues of the 23C3 Fab and residues of the epitope peptide. The color coding is the same as above. The residues that participate in the hydrogen-bonding interactions are shown with ball-and-stick models. (c) An electrostatic potential surface of the 23C3 Fab at the interface. The Fab accommodates the peptide with great structural and chemical complementarity. (d) The extensive hydrophobic interactions between the Fab and the key residue TrpP43 of the epitope peptide. Residues AlaL34 of CDR L1, PheL91 of CDR L3, MetH102 of CDR H3, and TyrL36, LeuL46, and TyrL49 of FWR L2 form a deep hydrophobic pocket to accommodate TrpP43 of the peptide. (e) The hydrophilic recognition of AspP47 by the Fab. AspP47 makes hydrogen-bonding interactions with SerH53, AsnH56, and ArgH52. It also forms electrostatic interactions with residues ArgH50 and ArgH52 of CDR H2. The color coding is the same as in (a).