Figure 1.
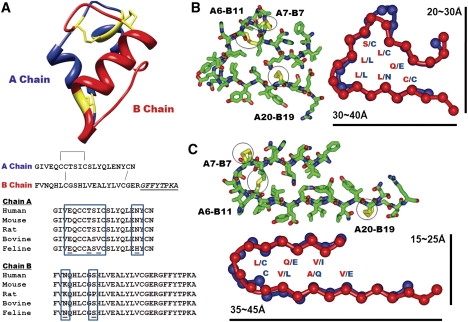
Insulin monomer structure and β-solenoid-based monomeric subunit models for the insulin amyloid fibril. (A) Insulin monomer structure (PDB code 1GUJ), with the sequences of chains A and B. One intrachain and two interchain disulfide bridges are shown in yellow in the structure and by connecting lines in the sequences. The C-terminal region of chain B, underlined and in italic, is not involved in amyloid fibrillization. Multiple sequence alignment of the insulin sequences from five different mammalian species is shown, with sequence variations in the boxes. (B and C) Cross-sectional views of insulin β-solenoid monomeric models, including the C-terminally truncated β-helix (B) and β-roll (C) insulin monomeric subunit models, based on templates from 1HV9 (segment 293–323) and 1VH4 (segment 230–274), respectively. Stick figures are shown with the side chains, with disulfide bridges in yellow. Schematic figures are shown with the amino acid residues facing inside, with approximate dimensions of the structures. Chains A and B are shown in blue and red, respectively.
