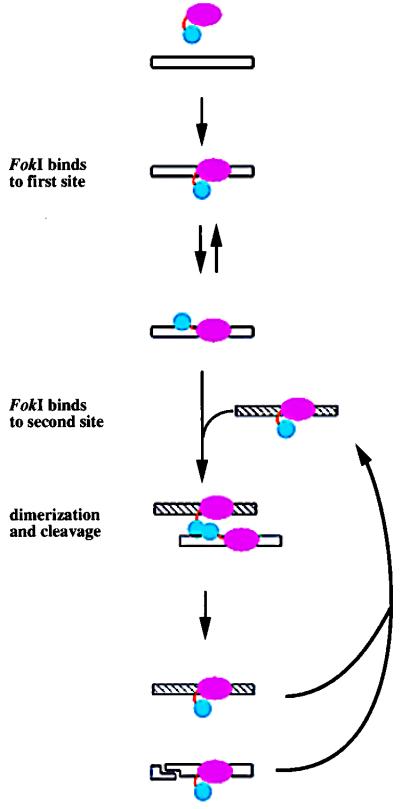
Figure 6.
A model of FokI cleavage. First, a FokI monomer binds DNA at its recognition site. Upon binding and in the presence of Mg2+, the cleavage domain dissociates from the recognition domain. A second FokI molecule, bound to another recognition site, dimerizes with the first molecule through their cleavage domains and catalyzes cleavage at the first site. After cleavage, the two FokI molecules dissociate from the DNA or they remain bound and catalyze additional cleavages by dimerizing with FokI molecules bound to other sites.