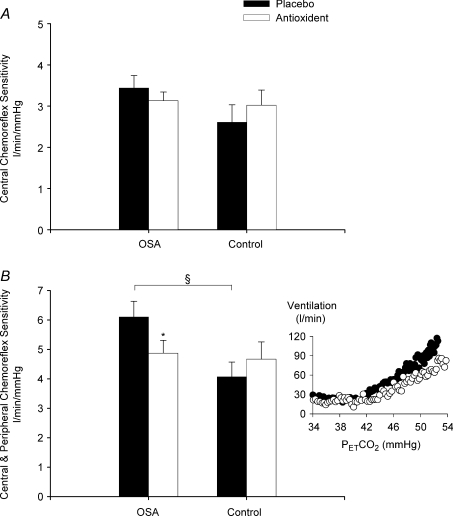
Figure 4. Chemoreflex sensitivity measures following intermittent hypoxia in OSA and control participants after administration of the placebo and antioxidant cocktail.
Bar graphs showing the average chemoreflex sensitivity obtained from the rebreathing trials completed while oxygen was maintained at 150 mmHg (central chemoreflex, A) or 50 mmHg (central and peripheral chemoreflex, B) after exposure to intermittent hypoxia during the placebo (filled bars) and antioxidant trials (open bars) in the OSA and control participants. Note that central and peripheral chemoreflex sensitivity during the placebo trial was significantly greater in the OSA participants compared to control. In addition, note that central and peripheral chemoreflex sensitivity following antioxidant administration was significantly reduced compared to placebo. A raw example of the reduction in central and peripheral chemoreflex sensitivity (i.e. a reduction in the slope of the minute ventilation response to carbon dioxide in the presence of hypoxia) in one OSA participant following antioxidant administration is shown in the inset figure. *Significantly different from placebo trial; §significantly different from control.