Table 2.
Arterial blood gases, pH, mean arterial blood pressure, heart rate during apnoea, baseline, +5 mmHg and +10 mmHg of CO2 in control and NCT anaesthetized adult male rats
| Control rats (n= 7) |
NCT rats (n= 7) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apnoea† | Baseline | +5 mmHg | +10 mmHg | Apnoea† | Baseline | +5 mmHg | +10 mmHg | |
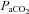 (mmHg) (mmHg) |
36.1 ± 2.2 | 39.6 ± 1.8 | 44.6 ± 1.9 | 49.3 ± 2.0 | 36.8 ± 2.1 | 39.7 ± 2.2 | 45.5 ± 1.8 | 50.3 ± 1.5 |
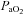 (mmHg) (mmHg) |
181 ± 13 | 173 ± 9 | 165 ± 9 | 170 ± 13 | 203 ± 15 | 204 ± 14 | 193 ± 16 | 193 ± 14 |
| pH | 7.38 ± 0.01 | 7.36 ± 0.01 | 7.32 ± 0.01 | 7.30 ± 0.01 | 7.39 ± 0.02 | 7.37 ± 0.02 | 7.33 ± 0.01 | 7.29 ± 0.01 |
| MAP (mmHg) | — | 106 ± 7 | 112 ± 6 | 112 ± 6 | — | 107 ± 13 | 118 ± 6 | 124 ± 8 |
| Heart rate (min−1) | — | 367 ± 30 | 373 ± 31 | 360 ± 25 | — | 364 ± 39 | 431 ± 10 | 433 ± 11* |
| Body weight (g) | 620 ± 19 | 613 ± 20 | ||||||
Arterial blood gases in this column correspond to values at apnoeic threshold when phrenic nerve activity ceases. 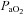 , arterial oxygen pressure;
, arterial oxygen pressure; 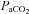 , arterial carbon dioxide pressure; MAP, mean arterial blood pressure. Values are expressed as means ±s.e.m.
, arterial carbon dioxide pressure; MAP, mean arterial blood pressure. Values are expressed as means ±s.e.m.
Significantly different from respective control value with P < 0.05.
