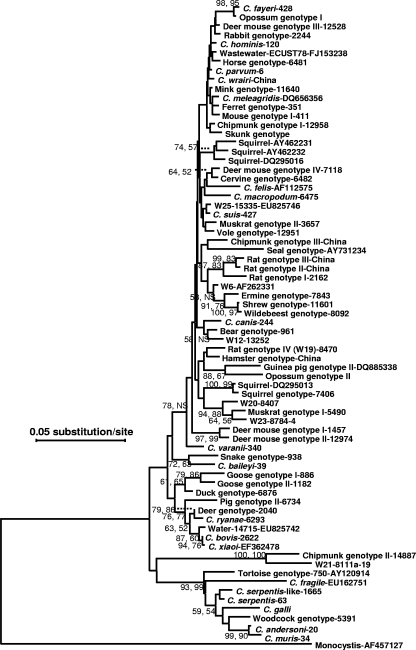
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic relationships among various Cryptosporidium species/genotypes from rodents in China and some known Cryptosporidium species and genotypes, as inferred by a neighbor-joining analysis of the partial (∼735 positions in the final alignment) SSU rRNA sequences based on distances calculated using the Tamura-Nei 93 model and adjusted with a gamma distribution (shape parameter, 1). Bootstrap values (in percentages) above 50 from 1,000 pseudoreplicates are shown for both the neighbor-joining (the first value) and maximum-parsimony analyses (the second value). ns, node with bootstrap values lower than 50%. Sequences from brown rats in Japan (23) are not included because of the lack of data from the 5′ end of the fragment under analysis. The multiple-sequence alignment of partial SSU rRNA sequences used in the generation of the phylogenetic tree is presented elsewhere (see the supplemental material).