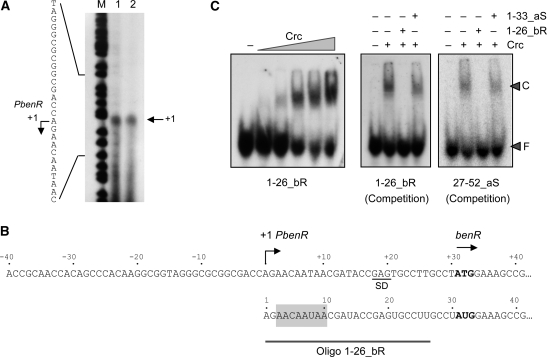
Figure 6.
Identification of the Crc binding site at benR mRNA. (A) Determination of the benR transcription start site by primer extension. Two identical primer extension reactions were analyzed on a urea–polyacrylamide gel, in parallel to a DNA sequence ladder obtained by chemical sequencing (the bands indicate C and T residues) (43). (B) Sequence of the promoter for the benR gene, indicating the transcription start site and the AUG initiation codon (in bold); the 5′-end of the benR mRNA is shown below; the sequence showing similarity to Crc binding site at alkS mRNA is shaded, and the RNA used in panel C is indicated. (C) Binding of purified Crc protein to 26 nt end-labelled RNAs spanning positions from +1 to +26 of benR mRNA (oligo 1–26_bR), or from +27 to +52 of alkS mRNA (27–52_aS). Left panel: the end-labelled 1–26_bR (0.1 nM) was incubated with 1 µg of tRNA as non-specific competitor, and in the absence (−) or in the presence of increasing concentrations of Crc (53, 106, 212, 425 or 850 nM). Competition experiments contained end-labelled oligonucleotide 1–26_bR (central panel), or end-labelled oligonucleotide 27–52_aS (right panel), Crc (212 nM), 1 µg of tRNA and, when indicated, a 50-fold excess of the unlabelled RNA oligonucleotides 1–26_bR (specific competitor) or 1–33_aS (non-specific competitor, corresponding to nts +1 to +33 of alkS mRNA).