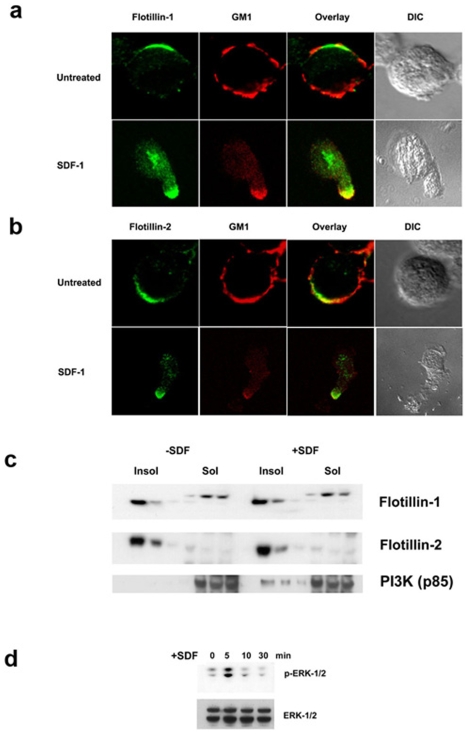
Figure 5. SDF-1α treatment induces reorganization of GM1- and flotillin-microdomains but does not affect DRM localization of flotillins in T cells.
a) Unstimulated (upper panel) and SDF-1a treated (lower panel) cells were stained with mouse anti-flotillin-1 (green) to detect flotillin-1. To detect the ganglioside, GM1, cells were stained first with Cholera toxin – B (CTX-B) subunit and then with rabbit anti- CTX-B antibodies (red). b) Unstimulated (upper panel) and SDF-1a treated (lower panel) cells were stained with mouse anti-flotillin-2 (green) to detect flotillin-2. GM1, on the other hand is detected by staining the cells first with Cholera toxin – B (CTX-B) subunit and then with rabbit anti- CTX-B antibodies (red). c) DRM fractions isolated from control (left) and SDF-1α treated (right) T cells were blotted for flotillin-1 (upper panel), flotillin-2 (middle panel) and PI3K (lower panel). Note that microdomain residency of flotillins is not affected during the treatment but PI3K specifically translocates to DRMs only upon chemokine stimulation. d) Whole cell lysates of SDF-1α treated cells for various times as indicated were boiled, electrophoresed and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. Upper panel: The membrane was then probed with anti-phospho-ERK1/2 antibodies. Increased ERK phosphorylation accompanied chemokine treatment at 5 min and decreases with time. Lower panel: Blotting with anti-ERK antibody shows the total ERK content.