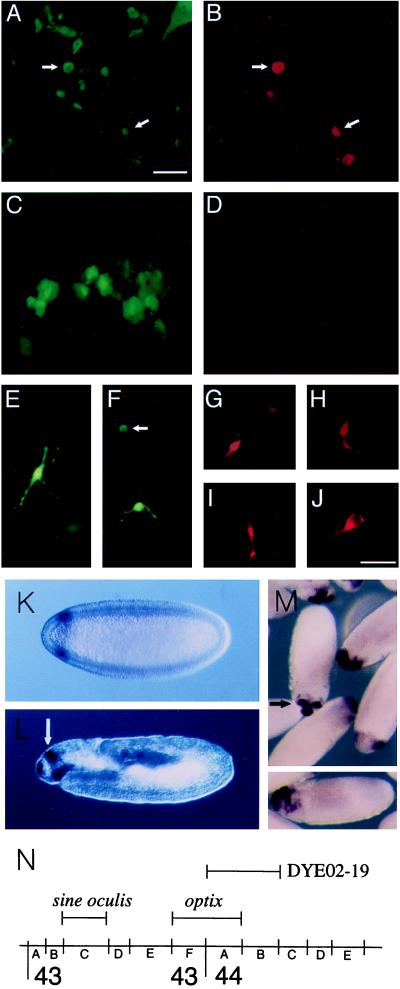
Figure 4.
Induction of neural retina markers in RPE; Expression and map position of the Drosophila optix gene. E7 RPE cells were transfected with 120 ng of cmvOptx2 and 40 ng of cmvGFP (A, B, and E–J) or with 160 ng of cmvGFP plasmid DNA alone (C and D). After 72 hr, cultures were stained with anti-visinin (rhodamine). Fluorescence detection with rhodamine-red (B, D, and G–J) or GFP-green (A, C, E, and F). A and B depict the same set of cells, as do C and D. The cell in E is visinin-negative. In F, the cell indicated by an arrow is also visinin-positive, whereas the other cell is visinin-negative. (G and H) Visinin-positive cells induced in E7 RPE, with the appearance of immature photoreceptors developing in culture. (I and J) Visinin and GFP-positive cells derived from post-hatch RPE. (Scale: bars in A and J = 50 μm for A–H and J; I = 100 μm.) Drosophila: In situ hybridization with optix probe was carried out with 0–12 hr Drosophila embryos. (K) Stage 5 (2.5 hr) blastoderm embryo, anterior to left, dorsal up, Nomarski optics. Circumferential band of optix expression, 93–85% egg length. (L) 11–12 (7 hr) embryo, before germ band contraction. Parasagittal optical section, orientation as before. Optix signal in dorsal, bilaterally paired structures (white arrow), the clypeolabrum (anterior end of embryo), and roof of the stomodeum. (M) In center, stage 13 embryo, view of dorso–anterior aspect, showing signal in paired dorsal sites and clypeolabrum. (M Lower) gastrulating embryo. Dorso–anterior expression of optix. (N) Map position of optix at 43F–44A and sine oculis, as determined by hybridization to polytene chromosomes. Bar indicates extent of YAC DYE02–19, which contains optix.