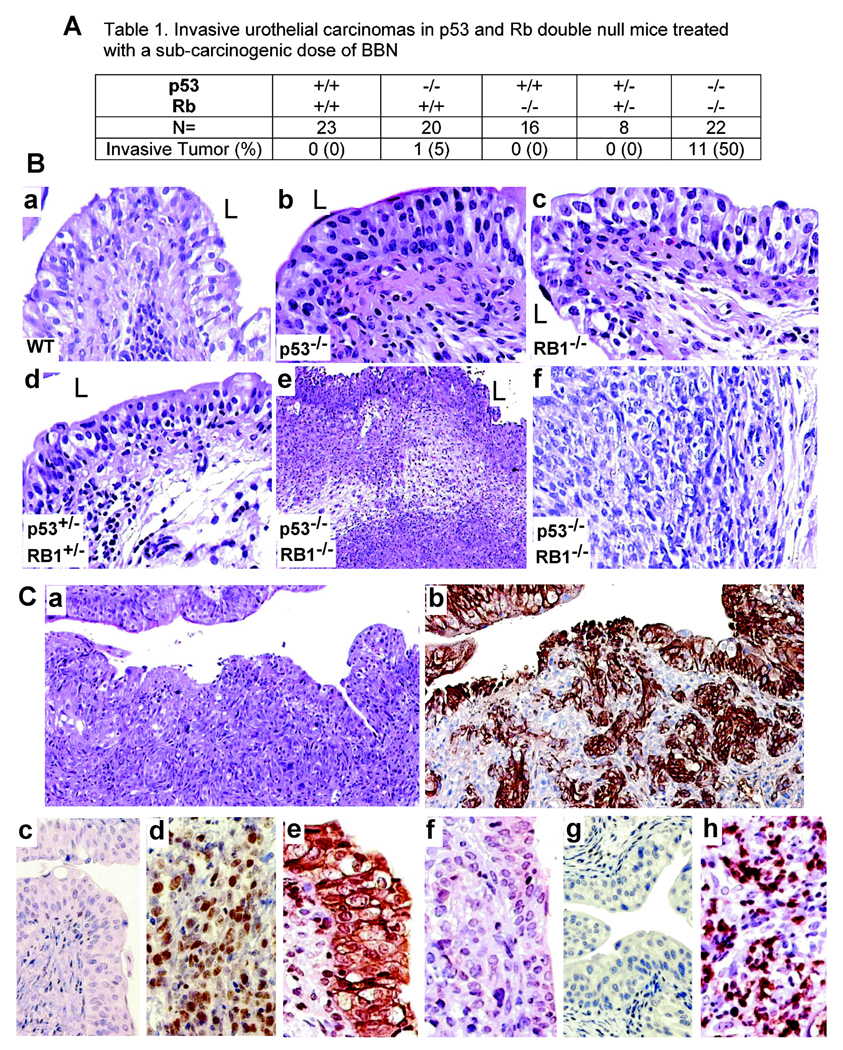
Figure 4. Susceptibility of the p53/RB1 null mice to a sub-threshold treatment of a bladder-specific carcinogen, BBN.
(A) Frequency of invasive urothelial carcinomas. (B) H&E-stained cross-sections of the urinary bladders from age-matched (3-month) wild-type (a), p53−/− (b), RB1−/− (c) and p53+/−/RB1+/− (d) mice all exhibiting slight urothelial dysplasia with inflammation and edema in the lamina propria. (e & f) a p53−/−/RB1−/− double null mouse exhibiting an invasive tumor. Magnification: a–d, f, 200 ×; e, 50 ×. (C) Characteristics of BBN-triggered muscle-invasive urothelial carcinomas. Invasive lesions in mice null for p53 and pRb (a; H&E) showed strong staining for basal cell keratins (b; consecutive section), over-expression of Ki67 (d), decreased expression E-cadherin (f) and over-expression of MMP9 (h), as compared with their paired wild-type controls (c, e & g). Magnifications: a and b, 50 ×; c–h, 200 ×.