Figure 1. Mutation of Lys-269 in cyclin D1 leads to increased cyclin D1 protein stability without the attenuation of cyclin D1 functions.
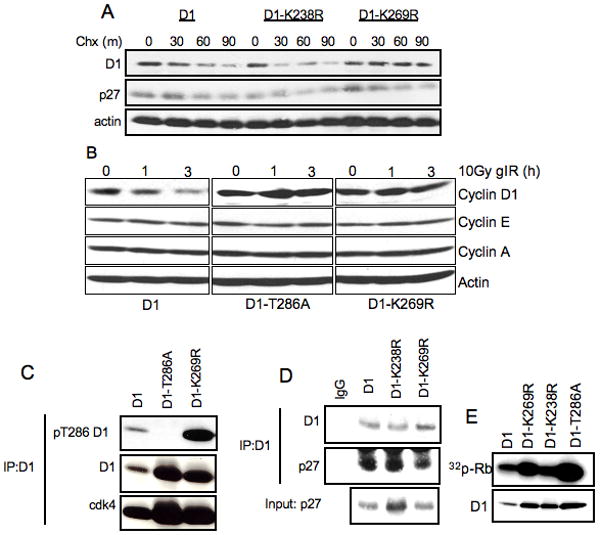
A. NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing wild-type cyclin D1, D1-K238R and D1-K269R were treated with 100μg/ml cyclohexemide for indicated periods of time. Cells were harvested and cyclin D1 protein levels were determined by immunoblot with D1-72-13G antibody. B. NIH 3T3 cells expressing wild type cyclin D1, D1-T286A, or D1-K269R were irradiated and harvested as indicated. Cyclin D1 levels were assessed by immunoblot. C. Cell lysates from NIH-3T3 cell lines stably expressing WT cyclin D1, D1-T286A and D1-K269R were used for immunoprecipitation of cyclin D1 with M2 agarose followed by immunoblot with phospho-Thr-286, D1-72-13G and cdk4 antibodies. D. Same as B, immunoblot with p27 antibody. E. Cyclin D1/cdk4 complexes were assembled in SF9 cells and used to phosphorylate recombinant GST-Rb, followed by autoradiography.
