Figure 3. In vivo ubiquitylation of D1-K269R.
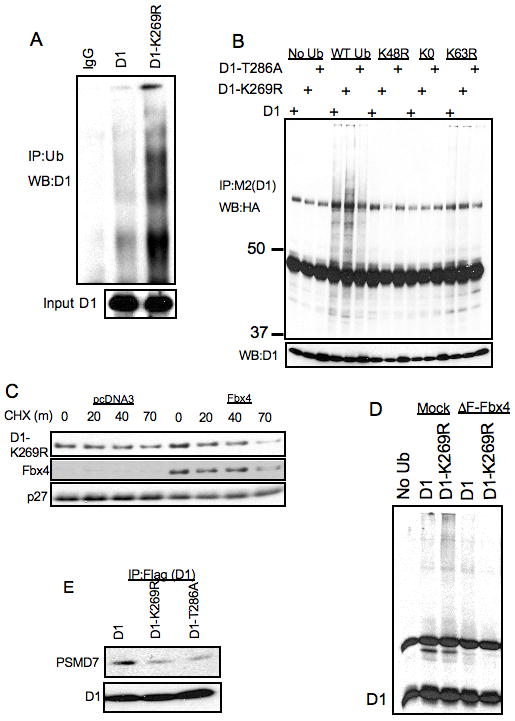
A. NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing WT and K269R cyclin D1 were treated with 10μM MG132 for 6 hours, proteins were lysed under denaturing conditions (50mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.4), 1% SDS and 5mM DTT). Proteins were precipitated with anti-ubiquitin antibody in the buffer containing 50mM Tris-HCL (pH 7.4), 250mM NaCl, 5mM EDTA and 0.5% NP-40 and separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by immunoblot with a cyclin D1 antibody. B. NIH-3T3 cells stably expressing WT cyclin D1, D1-T286A and D1-K269R cyclin D1 were transfected with WT, K48R, K0 and K63R ubiquitin constructs. 48 hours post-transfection cells were treated with 10 μM MG132 for 6 hours and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with M2 agarose followed by SDS-PAGE of protein complexes and immunoblot with anti-HA, cyclin D1 and Fbx4 antibodies. C. NIH-3T3 stably expressing D1-K269R were transfected with an Fbx4 expression vector. 48 hours post-transfections cells were used for cycloheximide chase assay at indicated time intervals. Cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot with cyclin D1, Fbx4 and p27 antibodies. D. 293T cells were transfected with ubiquitin, ΔF-Fbx4 and cyclin D1 constructs as indicated. 48 hours post-transfection cells were treated with 10 μM MG132 for 6 hours and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-cyclin D1 antibody followed by SDS-PAGE of protein complexes and immunoblot with the cyclin D1 antibody. E. Same as in B, followed by immunoblot with cyclin D1 and PSMD7 antibodies.
