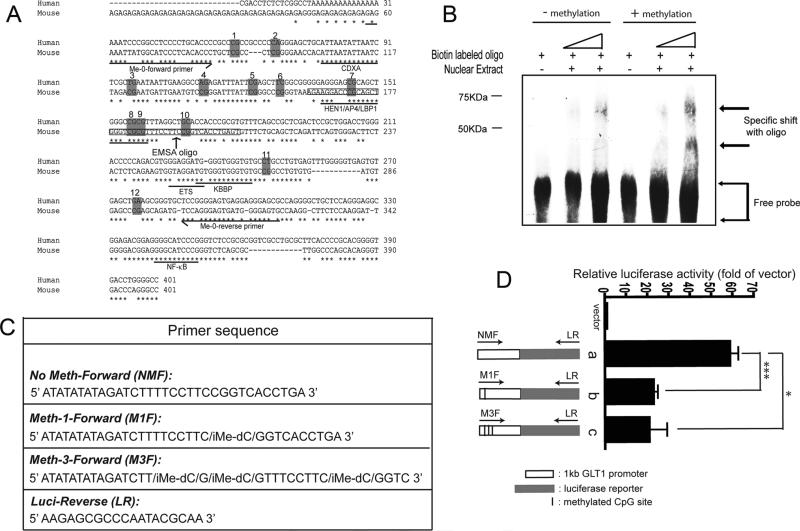
Fig. 4.
Methylation induced functional change of the GLT1 promoter. (A) Sequence analysis of putative transcriptional factors in Me-0 region of GLT1 promoter and human EAAT promoter. CDXA, chicken homeodomain protein; HEN1, Hua enhancer 1; AP4, activating enhancer binding protein 4; LBP1, upstream binding protein 1; KBBP, kappa B-motif binding phosphoprotein; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa B. Sequences were analyzed in sequence alignment program Mulan (http://mulan.dcode.org). (B) Methylation induced change in the nuclear factor binding EMSA assay of the methylated and unmethylated oligos was performed with nuclear extract from adult mouse cortex. (C) Primer sequence used for making a linear GLT1 promoter and luciferase reporter fragment from pGL4.14-PGLT1. iMe-dC: addition of methyl group on the specific cysteine site. (D) GLT1 promoter activity with site-specific methylation on selective CpG sites. a, wild type GLT1 promoter reporter; b, GLT1 promoter reporter with methylation on #10 CpG site; c, GLT1 promoter reporter with methylation on #8, #9, and #10 CpG sites. (n = 6, ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, One-way ANOVA and Bonferroni test).