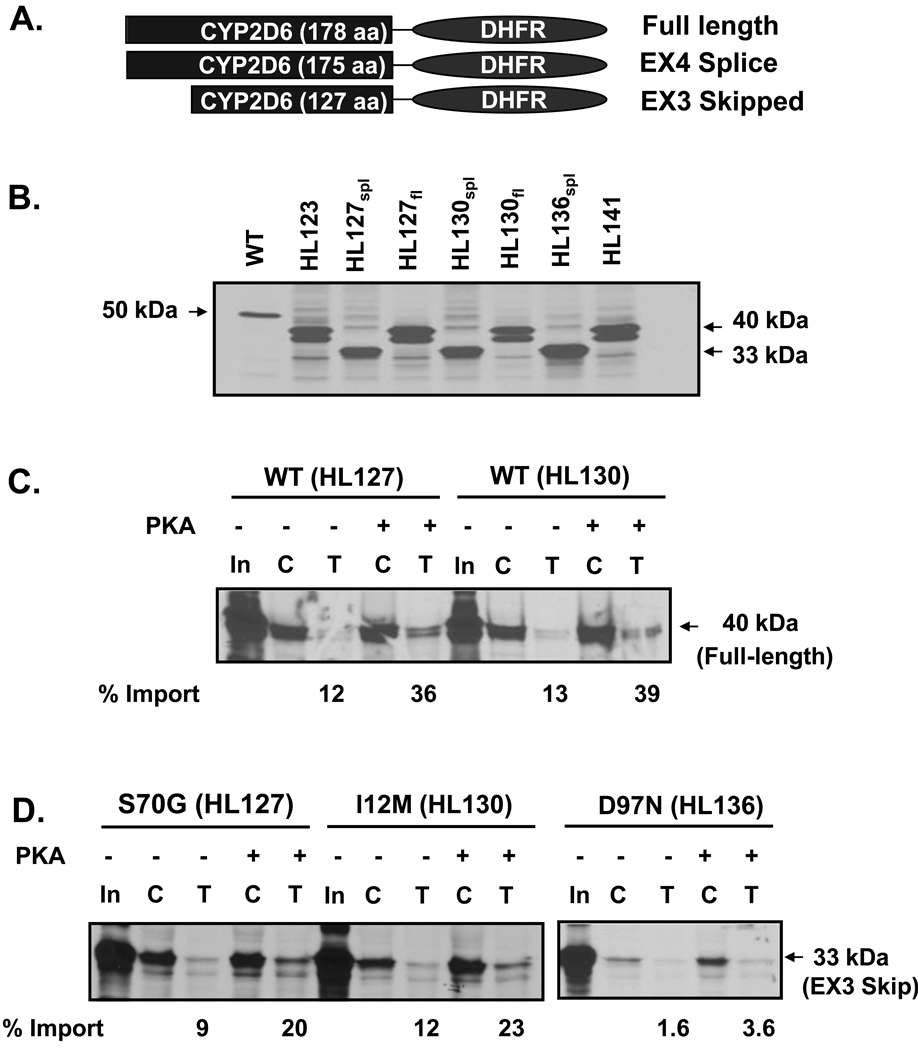
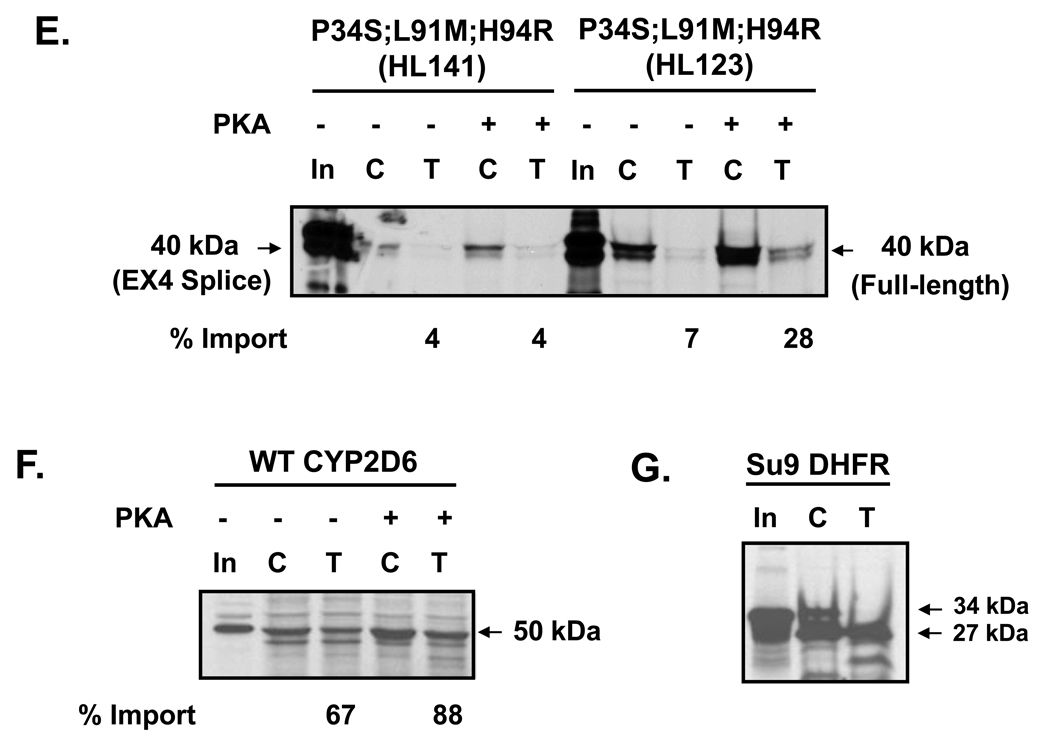
Fig. 4.
Effect of CYP2D6 genetic variation on mitochondrial targeting in vitro. (A) The N-termini of CYP2D6 variants (Table 1) were fused to DHFR through an EcoRI linker region. The full-length constructs were generated by fusing the N-terminal 178 amino acids of CYP2D6 to DHFR; the exon 3 skipped variants have 127 amino acids fused to DHFR; the exon 4 deletion variant is composed of 175 amino acids of CYP2D6 fused to DHFR. (B) Size comparison of each translation product used in the import experiment. 35S-labeled translation products were resolved by SDS-PAGE. (C–G) The 35S-labeled fusion proteins were used for in vitro import into isolated rat liver mitochondria. Trypsin digestion (150 µg/ml) of mitochondria was performed for 20 min on ice. Proteins (200 µg each) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and fluorography. “C” represents control experiments in which total protein bound and imported into mitochondria is present, “T” represents trypsin treated mitochondria in which only the protein imported into mitochondria is present. PKA refers to experiments in which the translation products were pre-incubated with the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A, 0.37 µg/50 µl reaction, prior to import. In the lanes marked “In,” 20% of the counts used as input for the import reactions have been loaded. Densitometric measurements were performed in order to determine the extent of import for each construct following trypsin treatment. This has been labeled as % import. The values were determined by calculating the level of each fusion protein in the mitochondria as a percentage of input. (C) Import of WT full-length CYP2D6-DHFR fusion constructs from HL 127 and HL130 are compared. (D) Import of exon 3-skipped splice variant constructs with varied point mutations (as labeled) from HL127, HL130, and HL136 are compared. (E) Import of constructs with P34S; L91M; H94R point mutations from HL123 and HL141 are compared. In HL123 the point mutations are present in the full-length construct, whereas in HL141 they are present alongside the exon 4 splicing defect in which 12 amino acids of exon 4 have been deleted. (F) Import of WT CYP2D6. (G) Import of positive control, Su9-DHFR, in which the presequence of subunit 9 of N. crassa F0F1 ATPase has been fused to DHFR.