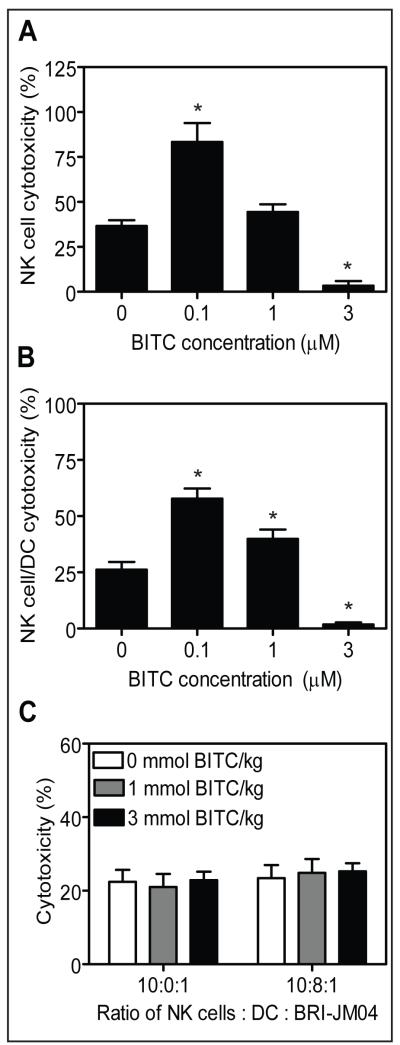
Fig. 5.
A, NK cells isolated from the spleen of wild-type FVB mice were cultured for 5 days in the absence or presence of 0.1, 1 or 3 μmol/L BITC and then tested for cytotoxicity against BRI-JM04 target cells. B, cytotoxicity of NK cells (isolated from the spleen of FVB mice) and dendritic cells (DC; isolated from the bone marrow of FVB mice) co-cultured for 5 days in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of BITC. The BRI-JM04 cells were used as target cells. In panels A and B, the experiment was repeated 3 times in triplicate and the results were consistent. Representative data from a single experiment are shown. Columns, mean (n= 3); bars, SE. *,P<0.05, compared with control by two-tailed Student’s t-test. C, ex vivo cytotoxicity of NK cells and DC isolated from spleen and bone marrow, respectively, of MMTV-neu mice of the control group, 1 mmol BITC/kg diet group or 3 mmol BITC/kg diet group against BRI-JM04 target cells. Columns, mean (n= 25 for the control group, n= 26 for the 1 mmol BITC/kg diet group, and n= 29 for the 3mmol BITC/kg diet group); bars, SE.