Figure 4. The N-terminal regulatory region of Raf kinases binds to the RBD region of RGS14.
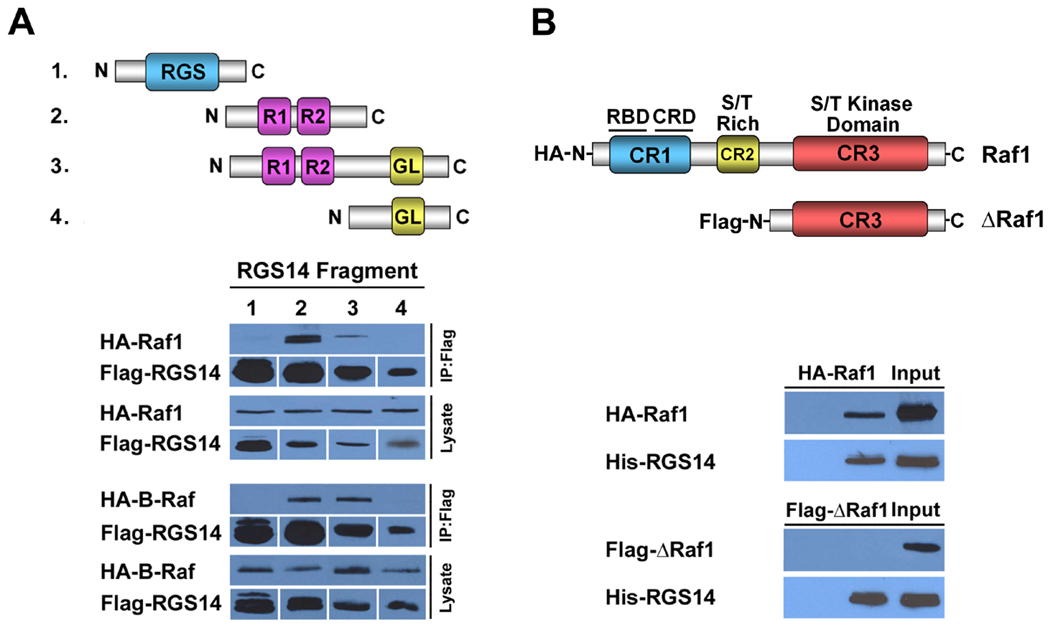
(A) The RBD region of RGS14 is required for Raf binding. Schematic diagram illustrating truncated Flag-RGS14 fragments used to co-immunoprecipitate with Raf kinases, as described in Experimental Procedures. RGS14 RBD domains are required for Raf binding. For immunoblots (below), HeLa cells were co-transfected with constructs expressing individual truncated Flag-RGS14 fragments together with HA-tagged Raf constructs (HA-Raf-1 or HA-B-Raf), respectively. Whole-cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Only RGS14 fragments containing the RBD regions are able to bind either Raf-1 or B-Raf. Cell lysates shown in the lanes represent 5% of the whole cell extracts used for IP. (B) The N-terminal regulatory region of Raf-1 is required for RGS14 binding. Schematic diagram illustrating full-length Raf-1 and a truncated Raf-1 fragment missing the regulatory domains (CR1, CR2) but containing a functional kinase domain. HeLa cell lysates containing either HA-Raf-1 or HAB- Raf were mixed with purified Trx-H6-RGS14 and subjected to protein interaction trap assays (Ni- NTA pull-down). Recovered proteins were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-Raf-1 antibody and anti-Flag (to detect RGS14) antibody, respectively. Results are representative of at least three separate experiments for each condition.
