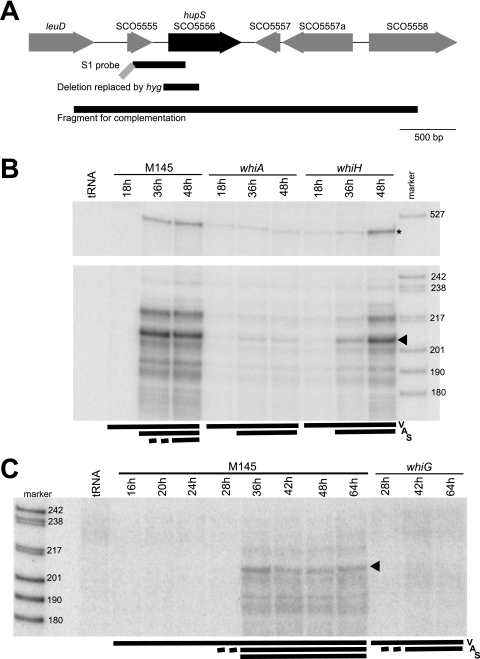
FIG. 1.
(A) Structure of the hupS region of the S. coelicolor chromosome. Locus tags from the S. coelicolor genome sequence are used (5). The extent of the probe used for S1 nuclease assays, the deletion in hupS that was replaced by Ωhyg to generate a knockout mutation, and the fragment that was used in complementation assays are shown below the schematic map as black lines. The gray diagonal line indicates an extension on the S1 probe that contains vector-derived sequence. (B and C) S1 nuclease protection assay of hupS transcripts. Total RNA was extracted from cultures grown on MS agar at the times indicated. The developmental stage at time of harvest is indicated by bars and letters V for vegetative mycelium, A for aerial mycelium covering colony surface, and S for spores being present. An equal weight of RNA was added to each S1 mapping reaction, and a control reaction with an equal weight of yeast tRNA was included in lanes labeled “tRNA.” The lanes labeled “marker” contain a set of DNA molecular weight markers (in base pairs). Panels B and C show different sets of RNA. The RNA preparations represented in panel C are identical to those previously used for mapping ftsZ and smeA promoters (2, 18). Panel B (top) shows protected fragments corresponding to the readthrough of transcription from promoters upstream of the probe (indicated by asterisk). The main protected band is indicated by arrowheads.