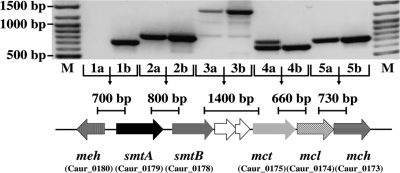
Fig. 3.
Organization of genes involved in the glyoxylate assimilation cycle. For catalyzed reactions (in parentheses) see Fig. 1. To amplify the intergenic regions of the cluster shown below, standard PCRs were performed with cDNA (a) and genomic DNA (b) as control. The positions of the amplified fragments are indicated by bars, and their expected sizes are given in bp. Lane M contained a 100-bp DNA ladder. meh, mesaconyl-C4-CoA hydratase (mesaconyl-C4-CoA (enoyl-CoA) hydratase) (reaction 13); smtAB, succinyl-CoA:(S)-malate CoA transferase subunits A and B (reaction 7); mct, mesaconyl-CoA C1-C4 CoA transferase (reaction 12); mcl, trifunctional (S)-malyl-CoA/β-methylmalyl-CoA/(S)-citramalyl-CoA (MMC) lyase (reactions 10 a, b, c); mch, mesaconyl-C1-CoA hydratase (β-methylmalyl-CoA dehydratase) (reaction 11). Between the genes of smtB and mct there are 2 ORFs of unknown function (no similar proteins are found in the database). For primers, see Table S1.