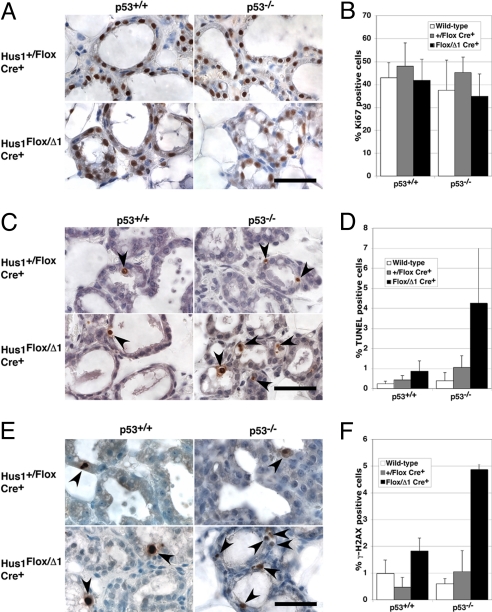
Fig. 4.
Increased genome damage and apoptosis in mammary glands from p53-deficient conditional Hus1 knockout mice. Sections from the fourth mammary gland of p53-deficient conditional Hus1 knockout mice at L2 were stained for Ki67 to assess proliferation, by TUNEL assay to detect apoptosis, or for γ-H2AX to detect DNA damage. Representative images of mammary glands stained for (A) Ki67, (C) TUNEL, or (E) γ-H2AX are shown. Arrows highlight positively-stained cells. (Scale bars, 40 μm.) Bar graphs show the average percentage of cells positive for (B) Ki67, (D) TUNEL, or (F) γ-H2AX staining, with error bars denoting standard deviation. Wild-type refers to Hus1+/+ Cre− p53+/+ and Hus1Flox/Flox Cre− p53+/+ or Hus1+/Flox Cre− p53−/−. Values for p53−/− mice are the mean of at least six fields from two animals. Data for Ki67, TUNEL, and γ-H2AX staining on sections from p53+/+ mice are the same as those shown in Fig. 2. The difference between the frequency of positively stained cells in Hus1Flox/Δ1 Cre+ p53−/− and Hus1+/Flox Cre+ p53−/− mice was significant for TUNEL (P = 0.021) and H2AX (P < 0.001) but not Ki67 (P = 0.059) assays as determined by Student's t-test.