Fig. 2.
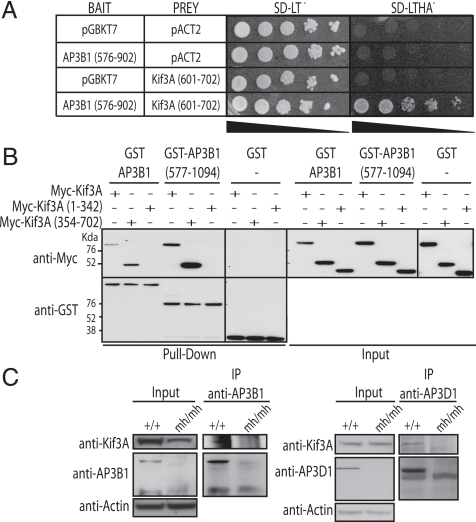
AP3B1 interacts with Kif3A. (A) Yeast two-hybrid interaction between AP3B1 (amino acid 576 to 902; in pGBKT7 vector) and the C-terminal non-motor domain of Kif3A (amino acid 601 to 702; in pACT2 vector). Yeast AH109 expressing both vectors were serially diluted and spotted on yeast synthetic media lacking either leucine and tryptophane (SD-LT−, to assess growth of cotransformed yeast) or leucine, tryptophane, histidine, and adenine (SD-LTHA−, to assess interaction strength), and grown at 30 °C for 3 days. (B) Interaction between GST-AP3B1 and Myc-Kif3A in mammalian cells. HeLa cells were cotransfected with Myc-Kif3A, Myc-Kif3A (1–342), or Myc-Kif3A (354–702) together with GST-AP3B1, GST-AP3B1 (577–1094), or GST vector control. Proteins were extracted 24 h after transfection and subjected to pull-down with glutathione beads. Interactions were detected by immunoblotting with an anti-Myc antibody (Top) and an anti-GST antibody (Bottom). The inputs are shown on the Right. (C) Endogenous AP3 complex interacts with endogenous Kif3A in mammalian cells. AP3B1 and AP3D1 were immunoprecipitated (IP) from wild-type MEF and mocha (mh/mh) cell lines and immunoblotted with antibodies against Kif3A, AP3B1, and AP3Da. Actin was used as loading control.