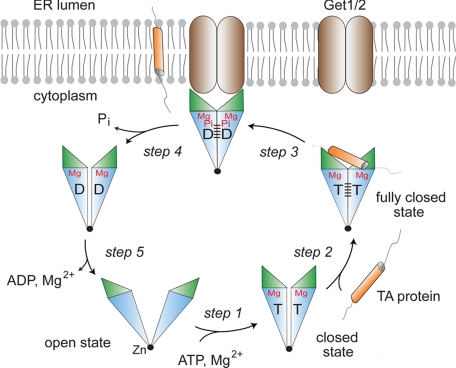
Fig. 6.
Model for TA binding and insertion. In the cytosol, the nucleotide-free (and ADP-bound) Get3 dimer is open. ATP binding to Get3 drives closure of the dimer (step 1) and allows TA protein binding. TA binding induces the fully closed hydrolysis-competent state (step 2). Get1/2 receptor docking occurs before or after ATP hydrolysis, with ADP and inorganic phosphate staying trapped in the closed active site (step 3). After TA protein release, inorganic phosphate is released and Get3 dissociates from the Get1/2 receptor (step 4). The Get3 dimer adopts an open structure on release of Mg2+ (step 5).