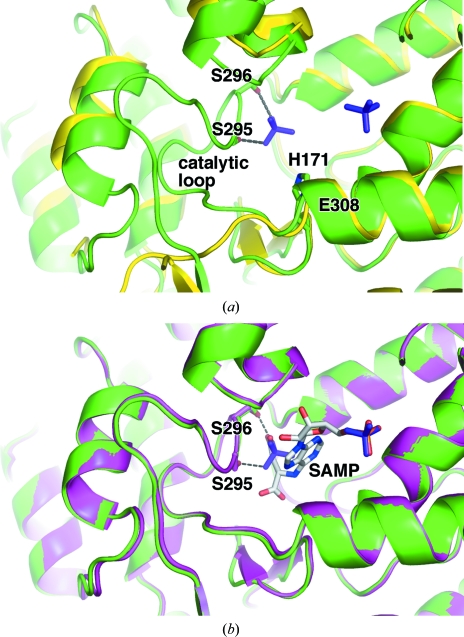
Figure 2.
E. coli ASL adopts a substrate-bound conformation with bound phosphates. (a) Overlay of the phosphate-bound enzyme (green) with the unliganded enzyme (PDB code 2pts; yellow). Hydrogen bonds between the phosphate ion and the side chains of Ser295 and Ser296 contribute to the stability of the catalytic loop and are shown as dotted lines. Most of the loop is absent in the apoenzyme structure. In the phosphate-bound enzyme structure the additional catalytically important residues, His171 and Glu308 are labelled. The side chain of Glu308 is hidden from view. (b) Overlay of the phosphate-bound enzyme (green) with the substrate-bound H171A mutant (PDB code 2ptr; magenta). Phosphate ions (purple) and SAMP (light grey) are shown in stick representation. Ser295, Ser296 and SAMP are labelled.