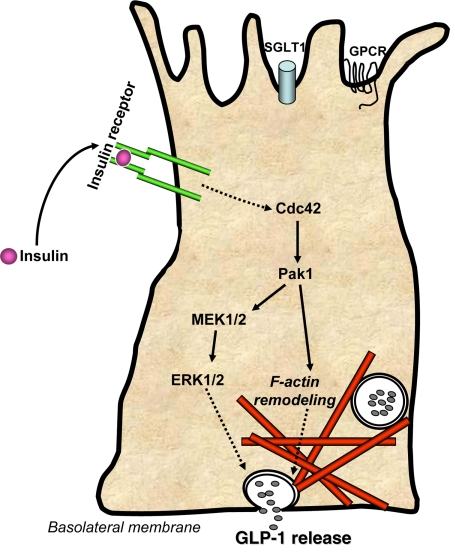
Figure 1.
Schematic model of insulin-induced GLP-1 release from intestinal L cells. Insulin binds to insulin receptors present on L cells to trigger the activation of Cdc42 within 10–15 min. Cdc42 expression is required for subsequent activation of Pak1 and MEK1/2 signaling cascades. Pak1 activation proceeds to induce F-actin remodeling, whereas MEK1/2 signals downstream to ERk1/2, with both pathways resulting in release of GLP-1. Insulin signaling may occur at alternate surfaces based upon reports of insulin receptor localization (25,26). Nutrient sensing through sodium-dependent glucose transporter-1 (SGLT1) and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) occurs as nutrients pass cell in the intestinal luminal surface (top).