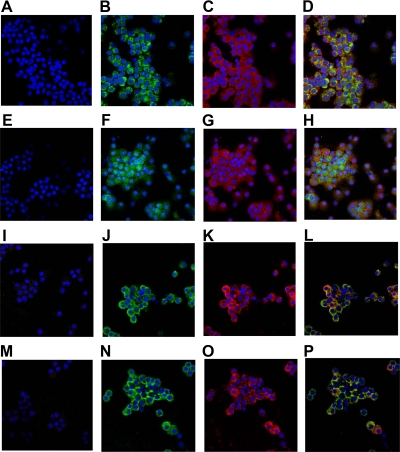
Figure 3.
Immunolocalization of GLUT9 in dispersed mouse and human islets. A–H, GLUT9 expression in dispersed mouse islets. Isolated mouse islets were dispersed into single cells by trypsin digestion and analyzed by immunohistochemistry using primary antibodies to mGLUT9a (B and D) or mGLUT9b (F and H) followed by incubation with Alexafluor-488 conjugated secondary antibody (green). β-Cells within the population were identified using a primary antibody to insulin followed by incubation with an Alexafluor-546 conjugated secondary antibody (red) (C and D, G and H). Nuclei were visualized by TO-PRO-3 iodide staining (blue). I–P, GLUT9 expression in dispersed human islets. Human islets were dispersed into single cells by trypsin digestion and analyzed by immunohistochemistry using primary antibodies to hGLUT9a (J and L) or hGLUT9b (N and P) followed by incubation with Alexafluor-488 conjugated secondary antibody (green). β-Cells within the population were identified using an antibody to insulin followed by incubation with Alexafluor-546 conjugated secondary antibody (red) (K and L, O and P). Nuclei were visualized by TO-PRO-3 iodide staining (blue). Rabbit IgG was used as a negative control (A, E, I, and M). Results are representative of three independent experiments.