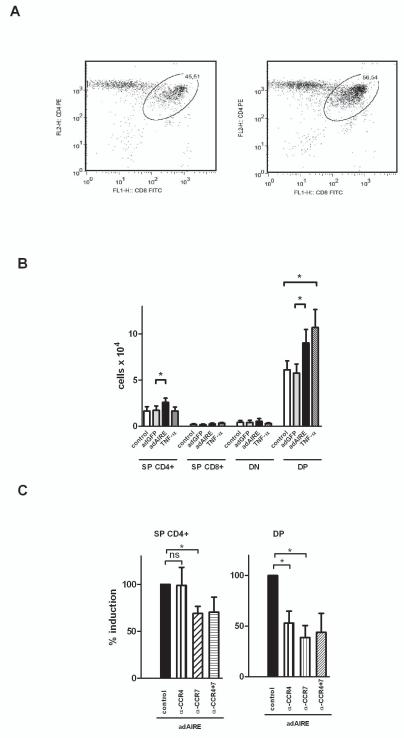
Fig.5.
Aire-induced CCR4 and CCR7 ligand expression results in increased chemotaxis of double-positive (DP) and single positive (SP) CD4+ thymocytes. Thymic epithelial cell-line TEC 1C6 was infected with either negative control, Ad-GFP (adGFP) or Ad-Aire-GFP (adAIRE) and, 48 h later, the cell supernatants were used as chemotactic stimuli for thymocytes in Transwell chemotaxis assay. Supernatants from TNF-α treated 1C6 were used as a positive control. The migrated cells were stained for CD4, CD8, and CD45 and analyzed by FACS. (A) Representative FACS plot of migrated thymocytes towards Ad-GFP vs Ad-Aire-GFP infected 1C6 cells. (B) Mean values with S.E.M of SP, double negative (DN), and DP thymocytes after migration towards the 1C6 cells infected with adGFP, adAIRE, negative control or TNF-α treated cells. Aire overexpression induced a selective migration of the DP and SPCD4 thymocytes whereas Ad-GFP alone did not have any significant effect. TNF-α treated supernatants induced migration of DP thymocytes but not other cell types. (C) Mean values with S.E.M. of SP CD4+ and DP thymocytes after migration towards adAIRE infected 1C6 cells pre-treated with antibodies against CCR4 ligands (α-CCR4), CCR7 ligands (α-CCR7) or the combination of CCR4 plus CCR7 ligands (α-CCR4+7). The Aire-induced migration of DP cells was inhibited by both the CCR4 and CCR7 ligand antibodies, whereas the SP CD4+ cell migration was inhibited by the CCR7 but not CCR4 ligand antibodies. *, Student t-test, p<0.05; ns= not significant, n=4–5.