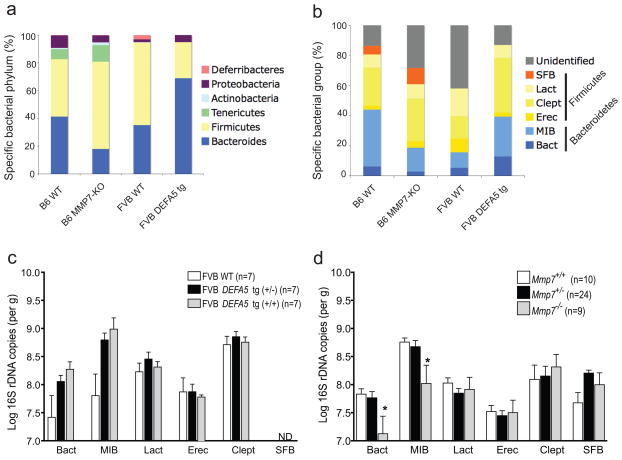
Figure 3.
Quantitative analysis of intestinal bacterial groups. a,b. Bacterial composition of the distal small intestines of Mmp7 −/− and DEFA5 tg (+/+) mice was determined by analysis of subclone sequences (a) and qPCR (b). Stacked graphs show relative percentages of dominant bacterial groups in the distal small intestine of offspring from Mmp7+/− and DEFA5 tg (+/−) breeding pairs with total bacterial sequences (a) or total bacterial copies as determined by amplification with universal bacterial primers (b) used as the denominator for subclone and qPCR analyses, respectively. c,d. Log number of total copies of specific bacterial 16S rDNA in the distal small intestine of each mouse was measured by pPCR. In offspring of DEFA5 tg (+/−) breeding pairs, the presence of SFB was not detectable (ND) by the reliable limits of detection by this assay. * P < 0.05.