Abstract
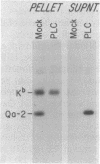
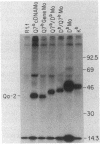
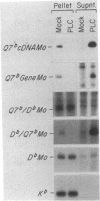
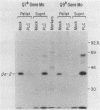
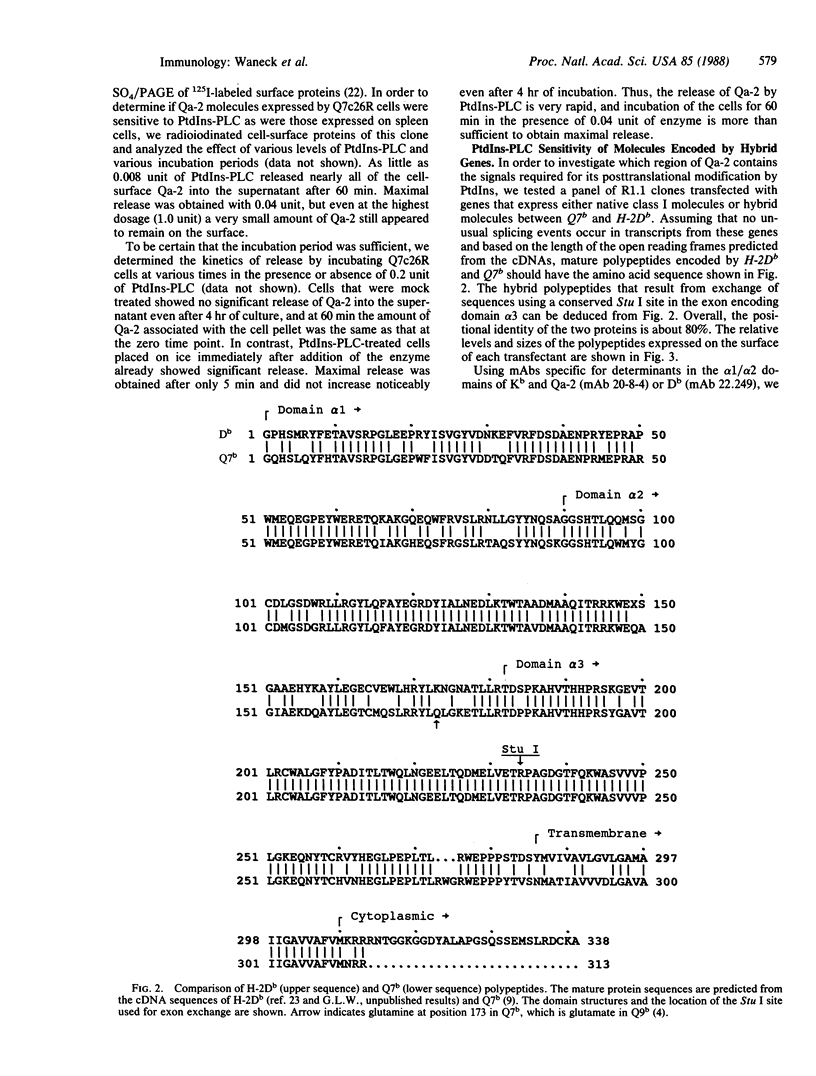
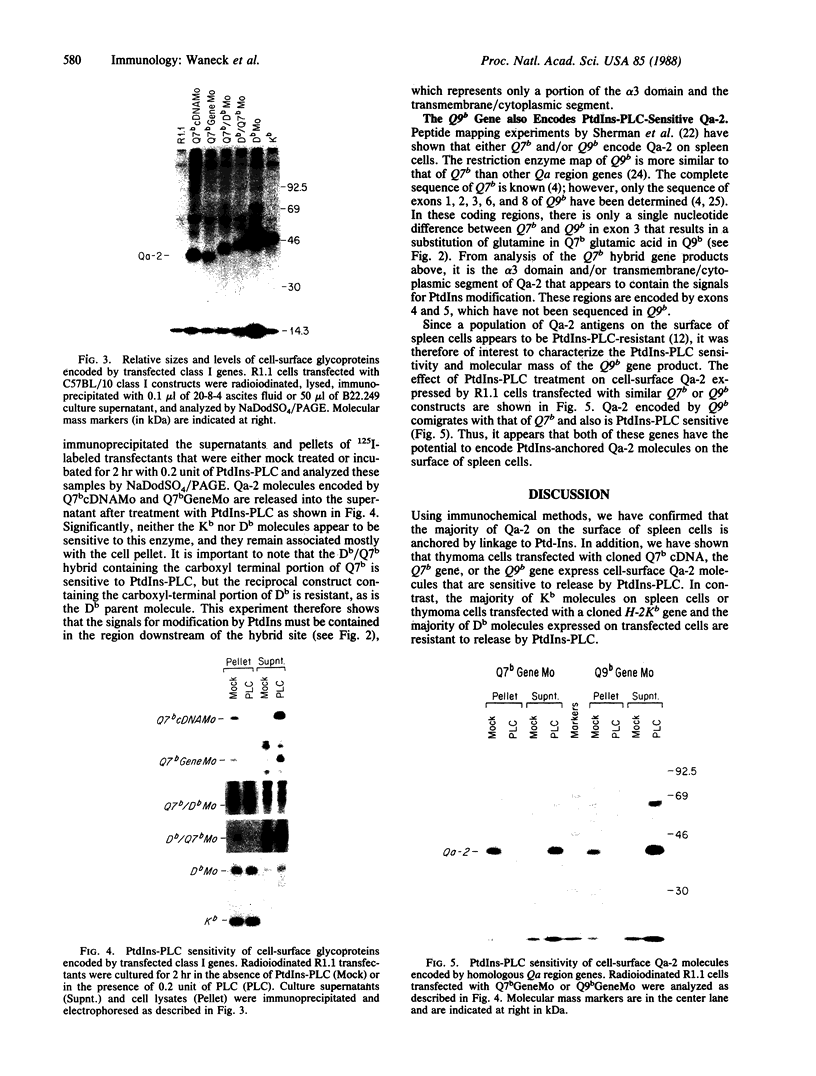
Proteins anchored in the membrane by covalent linkage to phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) can be released by treatment with purified PtdIns-specific phospholipase C (Ptd-Ins-PLC). A recent survey of leukocyte antigens using flow cytometry has shown that staining of certain Qa antigens was diminished after PtdIns-PLC treatment, but staining of structurally related H-2 antigens was not affected. Therefore, in this study, the sensitivity of cell-surface Qa-2, H-2Kb, and H-2Db to hydrolysis by PtdIns-PLC was investigated biochemically by immunoprecipitation of radioiodinated molecules from cell lysates or supernatants. Qa-2, but not H-2Kb, was released from the surface of PtdIns-PLC-treated C57BL/10 mouse spleen cells and recovered in the cell supernatants. Similar analysis of thymoma cells transfected with cloned C57BL/10 genes showed that cell-surface Qa-2 molecules encoded by a Q7b cDNA and the Q7b or Q9b gene were sensitive to hydrolysis by PtdIns-PLC, whereas the H-2Kb and H-2Db gene products were resistant. Using thymoma cells transfected with hybrid genes constructed by exchanging exons between Q7b and H-2Db, the signals for PtdIns modification were localized to a defined region of Qa-2. This region differs from H-2Db most significantly by the presence of a central aspartate residue in the transmembrane segment and in the length of the cytoplasmic portion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J., Uehara H., Martinko J., Nathenson S. G. Primary structure of a murine transplantation antigen. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):35–39. doi: 10.1038/291035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Hereld D., Shak S., Krakow J., Englund P. T., Nussenzweig V. A glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D in human serum. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2443973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Weiss E. H., Paulson M., Flavell R. A. Duplicated gene pairs and alleles of class I genes in the Qa2 region of the murine major histocompatibility complex: a comparison. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3203–3207. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner K., Hogan B. L., Flavell R. A. Transcription of H-2 and Qa genes in embryonic and adult mice. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1265–1271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. A., Allen H., Burkly L. C., Sherman D. H., Waneck G. L., Widera G. Molecular biology of the H-2 histocompatibility complex. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):437–443. doi: 10.1126/science.3726537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Soliz N. M., Saltiel A. R. Purification of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase C from liver plasma membranes: a possible target of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunter K. C., Germain R. N., Kroczek R. A., Saito T., Yokoyama W. M., Chan C., Weiss A., Shevach E. M. Thy-1-mediated T-cell activation requires co-expression of CD3/Ti complex. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):505–507. doi: 10.1038/326505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:149–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz D. M., Sherman D. H., Sitkovsky M. V., Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. Immunoprecipitation of cell surface structures of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes by clone-specific antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):573–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke H., Hämmerling G. J., Hämmerling U. Fine specificity analysis with monoclonal antibodies of antigens controlled by the major histocompatibility complex and by the Qa/TL region in mice. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:175–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Staphylococcus aureus. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):741–746. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Antoniou J., Robinson P. J. Structure and expression of genes encoding murine Qa-2 class I antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5920–5924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Weiss E. H., Kress M., Jay G., Flavell R. A. A nonpolymorphic class I gene in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Kruijer W., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Bierman A. J., de Laat S. W. Growth factor-like action of phosphatidic acid. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):171–173. doi: 10.1038/323171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Pösö H., Lapinjoki S. P., Gynther J., Andersson L. C. Growth signal transduction: rapid activation of covalently bound ornithine decarboxylase during phosphatidylinositol breakdown. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90557-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Uehara H., Ewenstein B. M., Kindt T. J., Coligan J. E. Primary structural: analysis of the transplantation antigens of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:1025–1052. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. III. Hybridoma antibodies reacting to antigens of the H-2b haplotype reveal genetic control of isotype expression. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser H., Oettgen H., Yeh E. T., Terhorst C., Low M. G., Benacerraf B., Rock K. L. Structural characterization of the TAP molecule: a phosphatidylinositol-linked glycoprotein distinct from the T cell receptor/T3 complex and Thy-1. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90593-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. A., Schöld M., Wallace R. B. The complete amino acid sequence of the murine transplantation antigen H-2Db as deduced by molecular cloning. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00364437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J. Two different biosynthetic pathways for the secretion of Qa region-associated class I antigens by mouse lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):527–531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrow S. O., Flaherty L., Sachs D. H. Serologic cross-reactivity between Class I MHC molecules and an H-2-linked differentiation antigen as detected by monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):21–40. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. H., Kranz D. M., Eisen H. N. Expression of structurally diverse Qa-2-encoded molecules on the surface of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1421–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloski M. J., Vernachio J., Einhorn G., Lattimore A. Qa gene expression: biosynthesis and secretion of Qa-2 molecules in activated T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2949–2953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernberg J., Low M. G., Flaherty L., Kincade P. W. Removal of lymphocyte surface molecules with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C: effects on mitogen responses and evidence that ThB and certain Qa antigens are membrane-anchored via phosphatidylinositol. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3877–3884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. S., Stroynowski I., Schiffer S. G., Hood L. Expression of hybrid class I genes of the major histocompatibility complex in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6245–6249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I., Forman J., Goodenow R. S., Schiffer S. G., McMillan M., Sharrow S. O., Sachs D. H., Hood L. Expression and T cell recognition of hybrid antigens with amino-terminal domains encoded by Qa-2 region of major histocompatibility complex and carboxyl termini of transplantation antigens. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):935–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I., Soloski M., Low M. G., Hood L. A single gene encodes soluble and membrane-bound forms of the major histocompatibility Qa-2 antigen: anchoring of the product by a phospholipid tail. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waneck G. L., Sherman D. H., Calvin S., Allen H., Flavell R. A. Tissue-specific expression of cell-surface Qa-2 antigen from a transfected Q7b gene of C57BL/10 mice. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1358–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuniga M. C., Hood L. E. Clonal variation in cell surface display of an H-2 protein lacking a cytoplasmic tail. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):1–10. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]