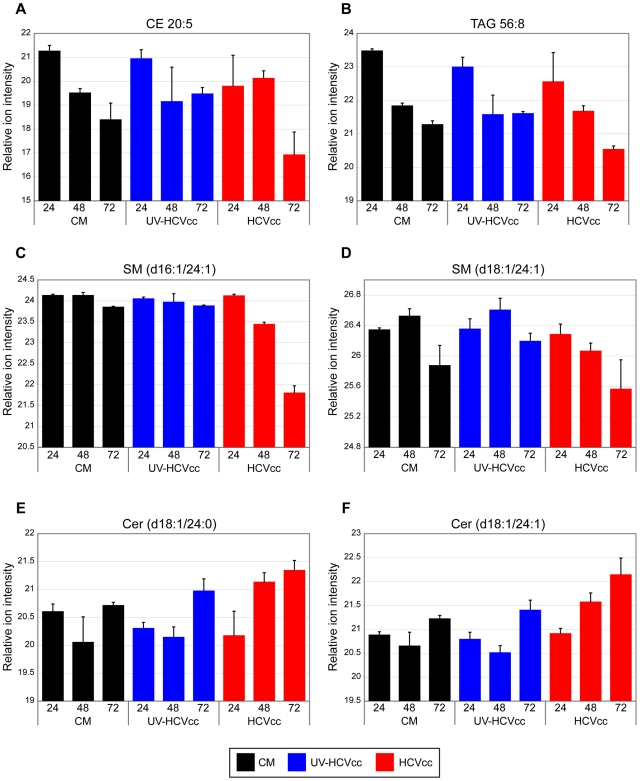
Figure 7. Representative examples of additional major lipid classes differentially regulated during HCV infection.
The relative ion intensity, log 2 scale, and standard deviation is plotted for various other lipid classes monitored 24, 48 and 72 h after infection with either HCVcc (red bars) or UV-HCVcc (blue bars) and using a time-matched mock (conditioned media, CM; black bars) as the reference. Panels A-D provide examples of HCV-associated decreases in the relative abundance of cholesterol ester (CE 20∶5), triacylglycerol (TAG 56∶8), and sphingomyelin (SM (d16∶1/24∶1) and SM (d18∶1/24∶1)) species, respectively. This contrasts with the HCV-associated increase in relative abundance of lipotoxic ceramide (CER) species shown in panels E and F (Cer (d18∶1/24∶0) and Cer (d18∶1/24∶1)), respectively. See legend of Figure 5 for details on the experiment representation and Supplementary Table S3 for a complete listing of the lipid features detected in this study.