Figure 1.
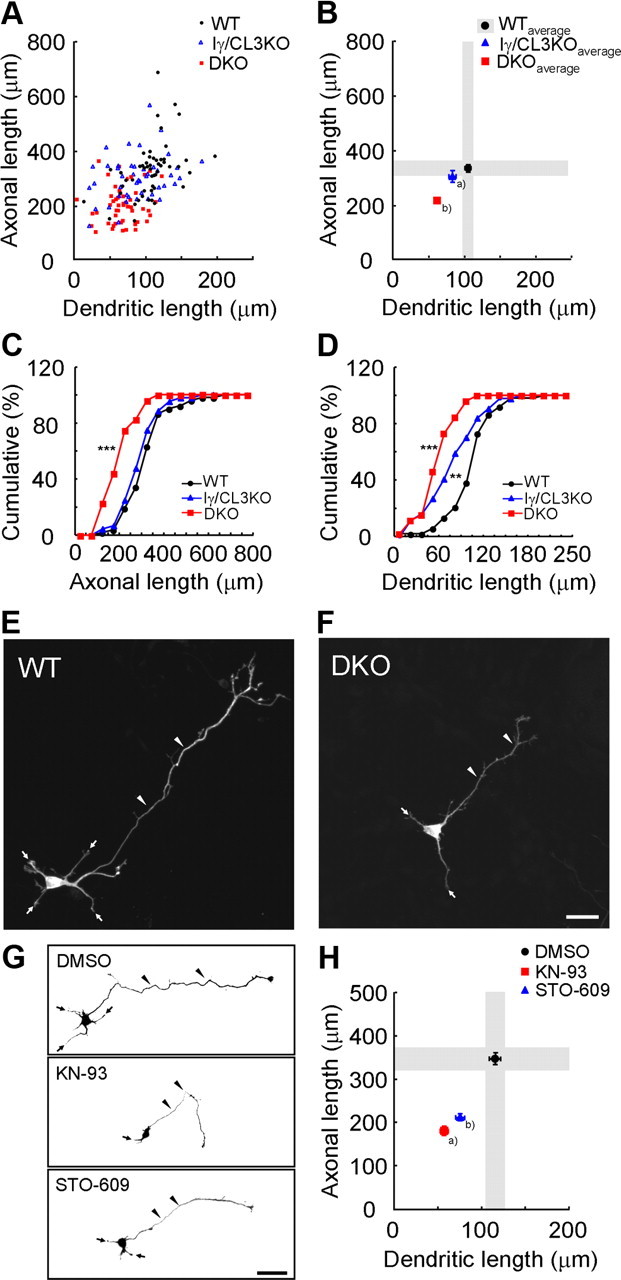
CaMKK-dependent CaMK cascades control cortical axonal and dendritic growth. A, B, A scattered plot (orthogonal plot) of data points (A) and averages (B) for both axonal and dendritic lengths obtained of individual neurons. Black circles, Wild type (WT). Blue triangles, Iγ/CL3 knock-out (Iγ/CL3 KO). Red squares, CaMKKα/β-double knock-out (DKO). Number of neurons: WT, n = 52; Iγ/CL3 KO, n = 44; DKO, n = 52. aDendrite, p < 0.01; bAxon, p < 0.001; dendrite, p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test comparison with WT). C, D, Cumulative probability analysis for total axonal length (C) and total dendritic length (D) in neurons from WT, DKO, and Iγ/CL3 KO mice. Number of neurons: WT, n = 52; DKO, n = 52; Iγ/CL3 KO, n = 44. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test comparison with WT. E, F, Cortical neurons (2 d in vitro) from CaMKKα/β-DKO mice (F) showed impaired growth of axons (arrowheads) and dendrites (arrows) compared with neurons from WT mice (E). Scale bar, 25 μm. G, Treatment with KN-93, a general CaMK inhibitor, and STO-609, a blocker of CaMKKα/β, the upstream kinases of all CaMKI/IV, from 6 to 48 h after plating impaired both axonal (arrowheads) and dendritic (arrows) growth. Scale bar, 50 μm. H, An orthogonal plot shows a quantitative analysis of axonal and dendritic morphometric parameters from each neuron. Number of neurons: DMSO, n = 48; KN-93, n = 43; STO-609, n = 48. a,bAxon, p < 0.001; dendrite, p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test comparison with DMSO).
