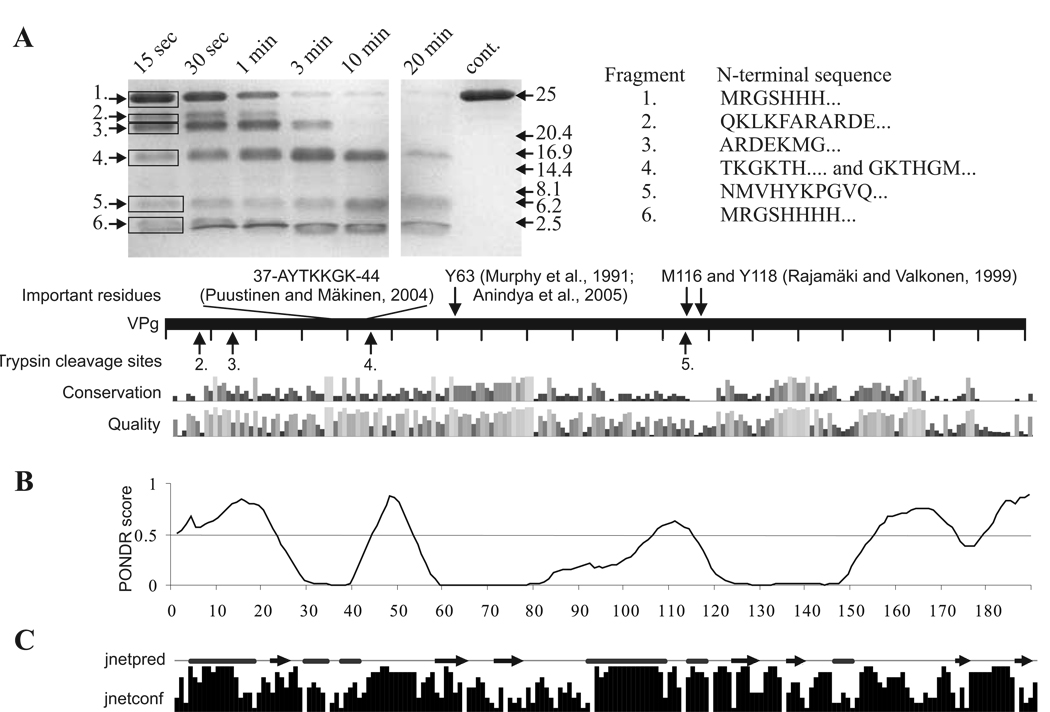
Fig 6.
Limited trypsin digestion of PVA VPg connected to bioinformatic analysis of potyviral VPg. The gel in (A) is a SDS -PAGE gel containing samples from limited trypsin digestion of PVA VPg collected at the given time points. N –terminal amino acid sequences of the numbered tryptic peptide fragments are given on the right and the trypsin cleavage sites detected are indicated by arrows under the bar representing the full-length PVA VPg. Some functionally important PVA VPg residues with references to the original publications are presented above the bar. Amino acid conservation within potyviral VPgs and quality of the conservation analysis in the potyVPg dataset are aligned below the bar. (B) Prediction of the disordered regions of VPg was performed with VLXT algorithm. Regions with a PONDR score above 0.5 are considered as disordered. Such regions were found mainly from the N- and C-terminal parts of PVA VPg. (C) Jnet consensus prediction of secondary structures was perforemed from 52 potyviral VPg sequences. Jnetpred line presents predicted α-helices (tubes) and β-sheets (arrows). Jnetconf column presents the confidence level of the predicted elements.