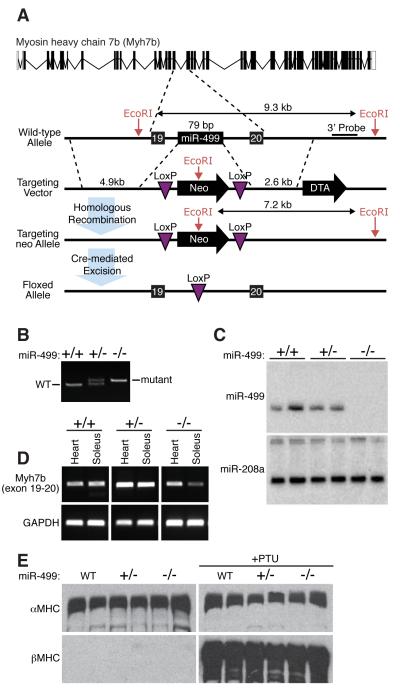
Figure 3. Generation of miR-499 null mice.
A) Strategy to generate miR-499 mutant mice by homologous recombination. The pre-miRNA sequence was replaced with a neomycin resistance cassette flanked by loxP sites. The neomycin cassette was removed in the mouse germline by breeding heterozygous mice to transgenic mice harboring the CAG-Cre transgene.
B) Detection of the miR-499 mutation by PCR. Primers flanking the loxP site in intron 19 of the Myh7b gene generate PCR products as indicated. The mutant band in the PCR reaction is larger than the wild type band due to replacement of the miRNA with a larger loxP site.
C) Detection of miR-499 and miR-208a transcripts by Northern analysis of hearts from wild-type, heterozygout and miR-499 mutant mice.
D) Detection of Myh7b expression by RT-PCR of RNA from heart and soleus of mice of the indicated genotypes using primers flanking intron 19. Deletion of miR-499 does not disrupt cardiac expression of Myh7b, while there is a slight decrease in expression in soleus.
E) Western analysis of α-MHC and β-MHC protein levels in hearts of neonatal mice of the indicated genotypes in the absence (left) and presence (right) of PTU. Two mice of each genotype were analyzed. Unlike miR-208, miR-499 is not required for up-regulation of β-MHC in response to PTU.