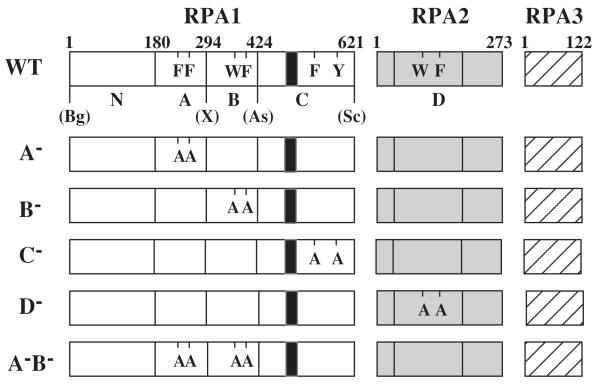
Fig. 1. Heterotrimeric RPA proteins used in this study.
The domain structure of wt RPA (Top) or the indicated mutant RPA protein is illustrated schematically. The RPA1 subunit consists of an N-terminal domain (N) and DBDs -A, -B, and -C while RPA 2 consists of DBD-D. RPA3 is wt in all RPA complexes. The amino acid residues comprising the domains of RPA1 are: N, 1 - 179; A, 180 - 294; B, 295 to 415; and C, 416 - 621. DBD-D is defined as amino acids 40-174 of RPA2. The positions of conserved aromatic residues within each DBD are indicated using single letter code. The following mutations are indicated: A−, F238A, F269A; B−, W360A, F385A; C−, F537A, Y586A; and D−, W101A, F143A. The unique restriction sites created in the wt RFA1 plasmid and their positions relative to the DBDs are presented: Bg, BglII; X, XhoI; As, Asp718; Sc, SacII; S, SalI; Bs, BsiWI. The black box located within DBD-C denotes the zinc-finger motif extending from position 486 to 508.